
Introduction
URL filtering and DNS filtering are two popular methods used to control and manage internet access within organizations. Both techniques aim to enhance security, productivity, and compliance with acceptable use policies. However, there are distinct differences between the two approaches. In this article, we will explore the features and benefits of URL filtering and DNS filtering to help you determine which method is better suited for your organization’s needs.
Introduction to URL Filtering and DNS Filtering
URL filtering involves blocking or allowing access to specific websites based on their URLs or web addresses. It compares the requested URLs against a predefined list of categories or criteria. This method provides granular control over internet access, allowing organizations to restrict access to inappropriate or non-work-related websites.
On the other hand, DNS filtering focuses on controlling internet access by blocking or redirecting requests based on domain names. It operates at the DNS level, intercepting DNS queries and providing responses that either allow or deny access to specific domains. DNS filtering is effective in preventing users from accessing malicious websites, phishing attempts, or other online threats.
While both URL filtering and DNS filtering offer benefits in terms of security and productivity, they have different strengths and limitations. URL filtering provides more precise control over website access, allowing organizations to define specific categories or criteria for blocking or allowing access. DNS filtering is a more efficient and scalable solution than inspecting individual URLs. It blocks entire domains or categories without the need for individual inspection.
In conclusion, the choice between URL filtering and DNS filtering depends on your organization’s specific requirements and priorities. Understanding the differences between these two methods will help you make an informed decision to enhance your network security and productivity.

URL Filtering Explained
Explanation of URL Filtering and its Mechanism
URL filtering is a method used to control and monitor internet access by blocking or allowing access to specific websites based on their URLs. It is a process that involves analyzing the URLs requested by users and comparing them against a predefined list of allowed or blocked websites. This list is usually created based on categories such as adult content, social media, gambling, or malware-infected sites.
URL filtering works by intercepting the user’s web requests and checking the URLs against a database of categorized websites. If the URL matches a blocked category, access to the website is denied. On the other hand, if the URL matches an allowed category, access is granted.
Pros and Cons of URL Filtering
URL filtering offers several benefits for organizations:
- Enhanced Security: By blocking access to malicious or inappropriate websites, URL filtering helps protect networks from potential threats such as malware, phishing attacks, and data breaches.
- Increased Productivity: By restricting access to non-work-related websites, URL filtering can help minimize distractions and improve employee productivity.
However, there are also some drawbacks to consider:
- Overblocking: URL filtering systems may sometimes block legitimate websites mistakenly categorized as harmful or inappropriate, leading to restricted access to useful resources.
- Evasion Techniques: Some users may find ways to bypass URL filters using proxy servers or virtual private networks (VPNs), undermining the effectiveness of the filtering system.
In conclusion, URL filtering can be an effective tool for organizations to control internet access and protect their networks. However, it is important to carefully configure and maintain the filtering system to avoid overblocking legitimate content while effectively blocking harmful websites.
DNS Filtering Explained
Explanation of DNS Filtering and its Mechanism
DNS filtering controls and manages internet access by blocking or allowing specific websites or content categories based on their domain names. It works by intercepting DNS requests made by users and redirecting them to a filtering server that analyzes the requested domain name against a list of blocked or allowed sites. If the domain is on the blocked list, the user is denied access, and if it’s on the allowed list, access is granted.
DNS filtering can be implemented at various levels, including network, device, or even individual user levels. It provides an effective way to enforce internet usage policies, protect against malware and phishing attacks, and prevent access to inappropriate or harmful content.
Pros and Cons of DNS Filtering
Like any technology, DNS filtering has its advantages and disadvantages. Here are some key points to consider:
Pros:
- Improved Security: DNS filtering helps protect networks from malicious websites, malware, and phishing attacks by blocking access to known threats.
- Content Control: It allows organizations to enforce acceptable use policies by blocking access to inappropriate or non-work-related websites.
- Bandwidth Optimization: By blocking access to bandwidth-intensive sites or content categories, DNS filtering can help optimize network performance.
Cons:
- Overblocking: There is a risk of legitimate websites being mistakenly blocked due to false positives in the filtering system.
- Evasion Techniques: Some users may find ways to bypass DNS filtering by using alternative DNS servers or virtual private networks (VPNs).
- Administrative Overhead: Implementing and managing DNS filtering requires ongoing maintenance and monitoring to ensure effectiveness.
In conclusion, DNS filtering is a powerful tool for controlling internet access and enhancing security. However, organizations should carefully evaluate its pros and cons to determine if it aligns with their specific needs and goals.
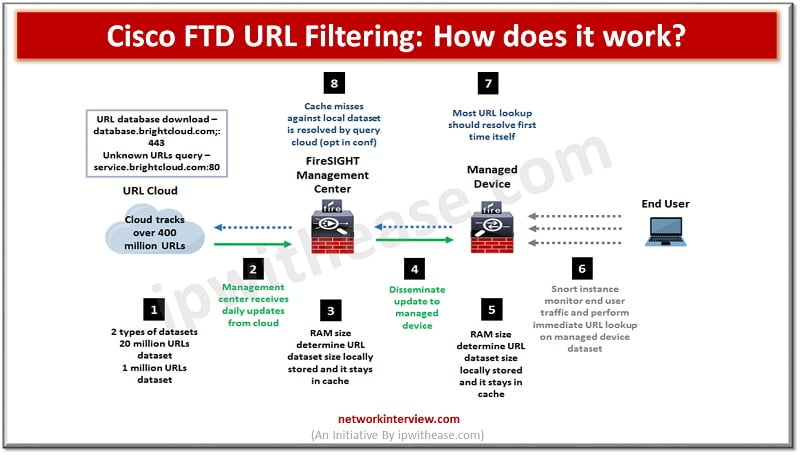
Comparing URL Filtering and DNS Filtering
Comparison of Features and Capabilities
URL Filtering and DNS Filtering are both effective tools for managing internet access and protecting against malicious content. However, they differ in terms of features and capabilities.
URL Filtering focuses on analyzing the content of URLs to determine whether they should be blocked or allowed. It provides granular control over specific websites or categories of websites, allowing administrators to create custom policies based on their organization’s needs. This makes URL Filtering a suitable choice for businesses that require precise control over internet access, such as those in highly regulated industries.
On the other hand, DNS Filtering works at the domain level by blocking or allowing access to entire domains or subdomains. It uses a blacklist or whitelist approach, where domains are categorized as either safe or unsafe. DNS Filtering is known for its simplicity and ease of implementation, making it a popular choice for small businesses or organizations with limited IT resources.
Comparison of Effectiveness and Accuracy
Both URL Filtering and DNS Filtering can effectively block access to malicious websites and prevent users from accessing inappropriate content. However, URL Filtering tends to be more accurate in its filtering capabilities due to its ability to analyze the content of specific URLs. This allows for a more targeted approach to blocking unwanted content.
DNS Filtering, on the other hand, may not be as accurate since it operates at the domain level. While it can block entire domains that are known to be malicious or unsafe, it may also block legitimate subdomains within those domains. This can result in false positives and potentially impact legitimate user access.
Comparison of Performance and Speed
When it comes to performance and speed, DNS Filtering has an advantage over URL Filtering. DNS Filtering is faster than URL Filtering because it processes requests at the network level instead of inspecting URLs and content.
The filtering methods’ performance and speed can vary based on the implemented solution and network infrastructure. Organizations should consider their specific needs and network requirements when choosing between URL Filtering and DNS Filtering.
In conclusion, URL Filtering and DNS Filtering offer different features, capabilities, effectiveness, and performance. Organizations should evaluate their specific requirements and consider factors such as accuracy, ease of implementation, and network performance when deciding which filtering method is better suited for their needs.
Use Cases for URL Filtering
Examples of Scenarios where URL Filtering is Preferred
URL filtering is a method used to control and restrict access to certain websites or web content based on predefined policies. It is commonly used in various environments to enhance security, productivity, and compliance. Here are some scenarios where URL filtering is preferred:
- Enterprise Networks: In corporate environments, URL filtering helps prevent employees from accessing malicious or inappropriate websites that could compromise network security or productivity.
- Educational Institutions: Schools and universities often use URL filtering to ensure that students are protected from accessing inappropriate content, while also complying with regulations related to internet safety.
- Public Wi-Fi Networks: Public Wi-Fi networks, such as those found in cafes or airports, can implement URL filtering to prevent users from accessing websites that may contain malware or illegal content.
Benefits and Limitations of URL Filtering in Different Environments
URL filtering offers several benefits, including:
- Enhanced Security: By blocking access to potentially harmful websites, URL filtering helps protect networks and devices from malware, phishing attacks, and other cyber threats.
- Increased Productivity: By restricting access to non-work-related websites, URL filtering helps employees stay focused on their tasks and reduces time wasted on personal browsing.
However, it’s important to consider the limitations of URL filtering as well:
- Overblocking: Sometimes, legitimate websites may be mistakenly blocked due to overzealous filtering policies, causing inconvenience for users.
- Evasion Techniques: Sophisticated users may find ways to bypass URL filters using techniques like proxy servers or virtual private networks (VPNs).
URL filtering has advantages in terms of security and productivity. However, it is crucial to properly set up and supervise the filtering policies to find the right balance between access and restrictions.
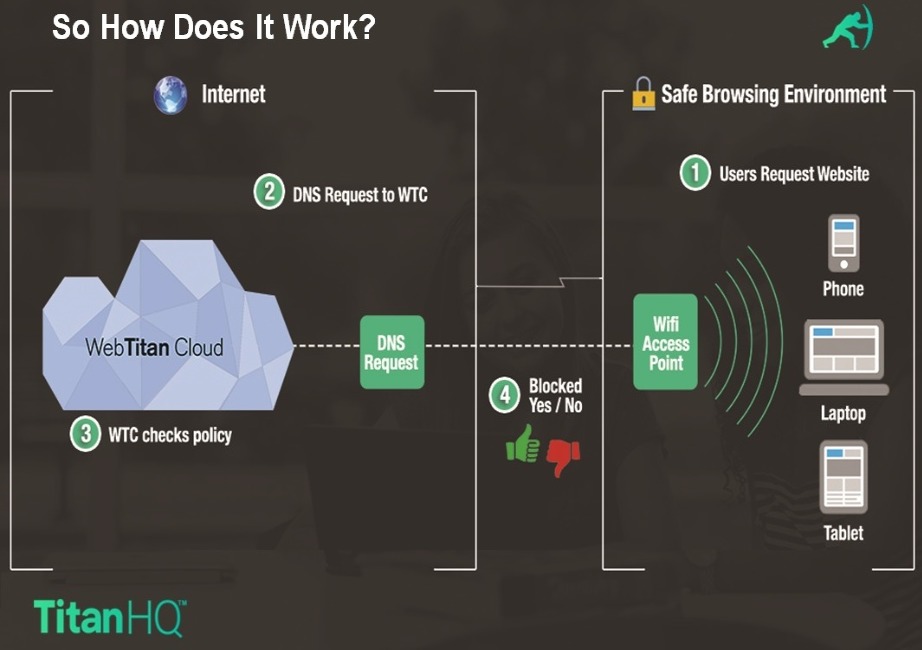
Use Cases for DNS Filtering
Examples of Scenarios where DNS Filtering is Preferred
DNS filtering is a powerful tool that provides organizations with the ability to control and manage internet access. Here are some scenarios where DNS filtering is preferred:
- Content Filtering: DNS filtering allows organizations to block access to websites that contain inappropriate or malicious content. This is particularly useful in schools, libraries, and workplaces where it is important to ensure a safe and productive online environment.
- Malware Protection: By blocking access to known malicious websites, DNS filtering helps protect organizations from malware infections. This is especially important for businesses that handle sensitive customer data or intellectual property.
- Compliance Requirements: Some industries have specific compliance requirements that mandate the filtering of certain types of content. DNS filtering enables organizations to meet these requirements and avoid potential legal and regulatory issues.
Benefits and Limitations of DNS Filtering in Different Environments
While DNS filtering offers several benefits, it also has some limitations depending on the environment in which it is implemented.
Benefits:
- Improved Security: DNS filtering helps prevent access to malicious websites, reducing the risk of cyberattacks.
- Increased Productivity: By blocking access to non-work-related websites, organizations can improve employee productivity.
- Bandwidth Optimization: Blocking access to streaming services and other bandwidth-intensive websites can help optimize network performance.
Limitations:
- Overblocking: Sometimes, legitimate websites may be mistakenly blocked due to false positives, resulting in user frustration.
- Circumvention: Determined users can bypass DNS filtering by using virtual private networks (VPNs) or proxy servers.
- Limited Visibility: DNS filtering only provides visibility into domain names and not the specific content being accessed.
In conclusion, DNS filtering is a valuable tool for organizations looking to control and manage internet access. However, it is important to consider the specific use cases and limitations before implementing DNS filtering in any environment.

Factors to Consider
Factors to Consider when Choosing between URL Filtering and DNS Filtering
When it comes to implementing web filtering solutions, businesses often face the dilemma of choosing between URL filtering and DNS filtering. Both methods have their own advantages and considerations that need to be taken into account. Here are some key factors to consider when making this decision.
Security, Functionality, Compatibility, and Cost
Security: The primary goal of web filtering is to protect the network from malicious websites and content. Both URL filtering and DNS filtering can provide security by blocking access to known threats. However, URL filtering offers more granular control as it filters based on specific URLs, while DNS filtering blocks entire domains.
Functionality: URL filtering allows for more precise control over website access by filtering based on specific URLs or categories. This can be beneficial for organizations that require strict control over internet usage. On the other hand, DNS filtering provides a broader approach by blocking entire domains, which can be more efficient for large-scale deployments.
Compatibility: Consider the compatibility of the web filtering solution with your existing infrastructure. URL filtering requires the installation of a proxy server or firewall, which may require additional hardware or software. DNS filtering, on the other hand, can be implemented at the DNS server level without the need for additional equipment.
Cost: Cost is an important factor to consider when choosing between URL filtering and DNS filtering. URL filtering solutions often require a higher upfront investment due to the need for additional hardware or software licenses. On the other hand, DNS filtering is generally more cost-effective as it can be implemented using existing infrastructure.
When deciding between URL filtering and DNS filtering, consider security requirements, functionality needs, compatibility with existing infrastructure, and cost. Assessing these factors will help businesses make informed decisions that align with their specific needs and goals.
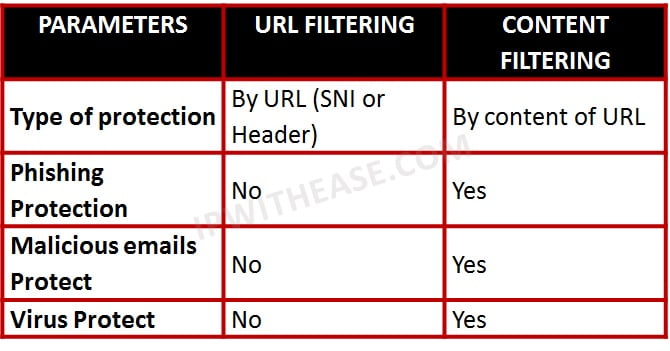
Conclusion
Summary of Key Points
URL filtering and DNS filtering are effective methods for controlling website access and protecting your network from malicious content.
URL filtering works by blocking or allowing specific URLs based on predefined categories or custom lists. It provides granular control over website access but requires constant updates to keep up with new websites and content.
DNS filtering, on the other hand, blocks access to websites based on their IP addresses. It offers broader protection by blocking entire domains or categories of websites, but it may also block legitimate content due to shared IP addresses.
Final Verdict: Which is Better
URL filtering and DNS filtering depend on your specific needs and priorities. If you require precise control over website access and are willing to invest time in maintaining URL lists, URL filtering may be the better option. However, if you prioritize broader protection and ease of implementation, DNS filtering may be more suitable.
URL Filtering or DNS Filtering?
Ultimately, the decision between URL filtering and DNS filtering should be based on your organization’s requirements, resources, and security goals. It is recommended to evaluate each method’s features, benefits, and limitations before making a decision. Additionally, consulting with IT professionals or security experts can provide valuable insights and help you make an informed choice.




