Overview of ISO 42001
ISO 42001 is a standard that helps organizations with sustainable management, promoting environmental and social responsibility in businesses. With increasing global awareness about sustainability, ISO 42001 aims to help organizations integrate sustainability into their core business practices. This standard provides structured guidelines, ensuring that companies recognize the significance of balancing economic, environmental, and social dimensions.
A company looking to reduce its carbon footprint can benefit from ISO 42001, which provides tools and practices to improve environmental impact and boost competitive advantage.
History and development of ISO 42001
The journey of ISO 42001 began in response to a growing collective demand for sustainable practices across various sectors. Key milestones in its development include:
- Initial Proposals (2015): The standard’s inception can be traced back to discussions focused on creating a unified global framework for sustainability.
- Drafting and Consultation (2017-2019): Multiple rounds of consultations involving industry experts and stakeholders led to a comprehensive draft.
- Final Approval (2021): Following reviews and refinements, ISO 42001 was officially released, marking a significant step towards standardized sustainability management.
ISO 42001 strengthens organizations’ commitment to sustainability and enables measurable impact across industries.
Understanding the Requirements of ISO 42001
Scope and purpose of ISO 42001
Delving into ISO 42001 reveals a clear focus on harmonizing sustainability efforts across diverse industries. The standard’s scope encompasses organizations of all sizes and sectors, emphasizing its universal applicability. Companies can leverage ISO 42001 to establish frameworks that:
- Promote sustainable practices
- Enhance stakeholder engagement
- Improve compliance with environmental regulations
A manufacturing firm can use ISO 42001 to create a sustainability plan that reduces costs and meets consumer demand for responsible practices.
Key terms and definitions in ISO 42001
Understanding ISO 42001 requires familiarity with specific terms. Here are a few:
- Sustainability: The ability to meet present needs without compromising future generations.
- Stakeholder: Any individual or group affected by the organization’s activities.
- Lifecycle Assessment: A technique to evaluate environmental impacts associated with all the stages of a product’s life.
These definitions serve as the foundation upon which organizations can build their sustainability strategies.
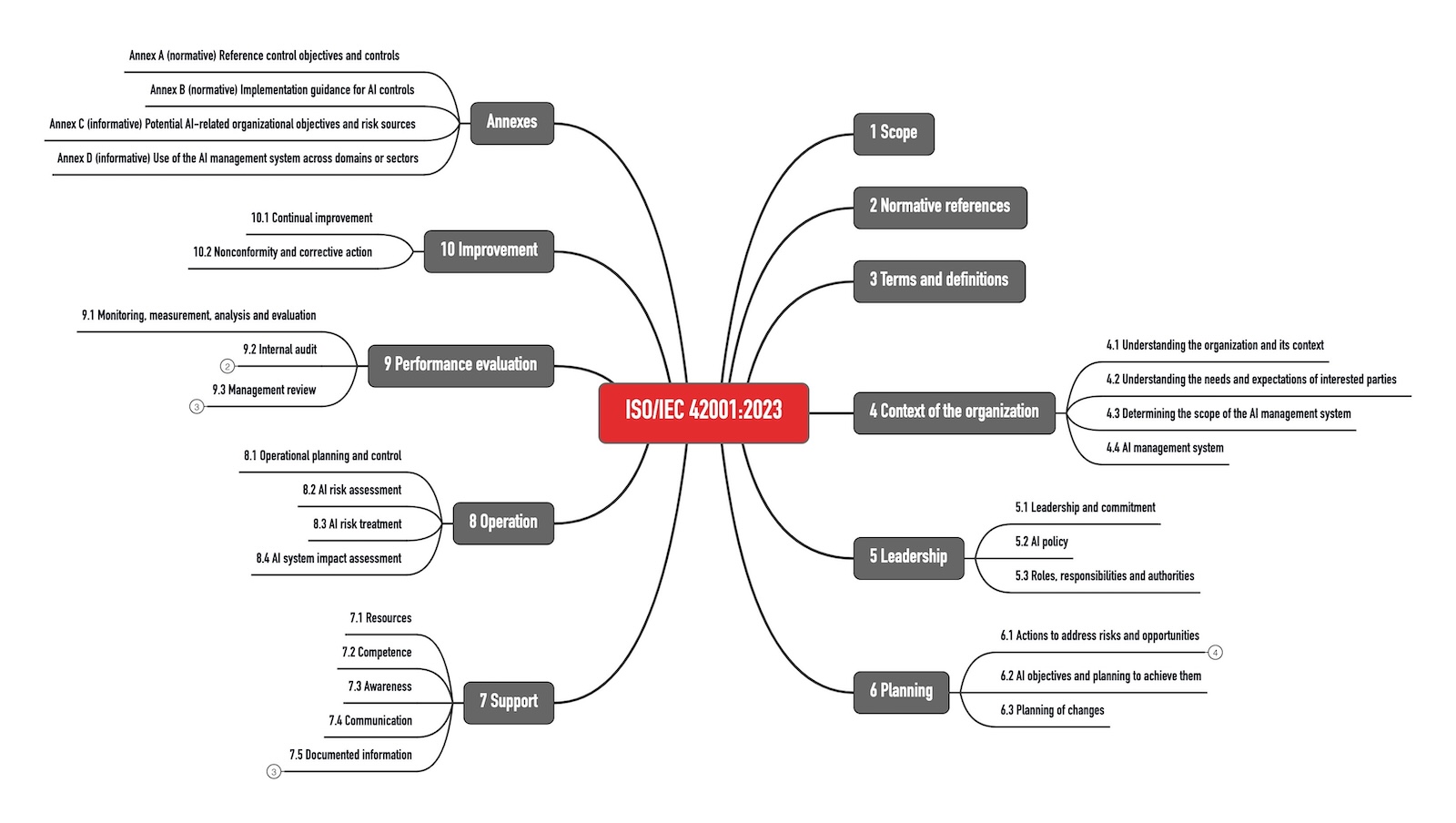
Structure and clauses of ISO 42001
ISO 42001 is systematically structured to facilitate implementation. It consists of key clauses that outline requirements such as:
- Leadership and Commitment: Engaging top management in sustainability initiatives.
- Planning: Identifying risks and opportunities related to sustainability.
- Performance Evaluation: Monitoring and measuring outcomes against established goals.
This well-defined structure allows organizations to systematically integrate sustainable practices into their operations, fostering a culture of continuous improvement.

Implementing ISO 42001
Steps to implement ISO 42001
Now that we have a foundational understanding of ISO 42001, it’s essential to discuss how to effectively implement it within an organization. The implementation process can be summarized in a series of structured steps:
- Leadership Buy-In: Secure commitment from top management to prioritize sustainability.
- Gap Analysis: Assess current practices against ISO 42001 requirements to identify areas for improvement.
- Strategy Development: Craft a sustainable management strategy aligning with organizational goals.
- Training and Awareness: Educate employees about ISO 42001 and its importance.
- Documentation and Process Adjustment: Document procedures and modify processes to comply with the standard.
- Implementation and Monitoring: Execute the plans and establish monitoring mechanisms to track progress.
A logistics company can improve route efficiency to cut emissions and save costs, demonstrating the effectiveness of this structured approach.
Benefits of implementing ISO 42001
The advantages of integrating ISO 42001 are multifold:
- Enhanced Reputation: Organizations become recognized leaders in sustainability.
- Increased Efficiency: Costs decrease by eliminating wasteful practices.
- Improved Compliance: Aligning with environmental regulations reduces legal risks.
An initiative to implement ISO 42001 could turn a company’s sustainability practices into a valuable market differentiator.
Challenges and considerations in implementing ISO 42001
However, challenges exist:
- Resistance to Change: Employees may be hesitant to alter established routines.
- Resource Allocation: Implementing the standard requires time, training, and investment.
- Complexity of Requirements: Navigating the clauses and documentation can be daunting for some organizations.
Organizations can maximize the benefits of ISO 42001 by proactively tackling these challenges, leading to a smoother transition to sustainable practices.
Certification Process for ISO 42001
Overview of the certification process
Once an organization is ready to embrace ISO 42001, the next logical step is pursuing certification. The certification process is both a journey and an evaluation, ensuring organizations adhere to the highest sustainability standards. It typically involves several phases:
- Preparation: After getting familiar with the standard, organizations may conduct internal assessments to ensure compliance.
- Application: An organization submits an application along with relevant documentation to a certification body.
- Audit Scheduling: The organization and certification body agree on audit dates.
- Certification Decision: Following successful audits, a certification decision is made based on compliance with ISO 42001.
For example, a mid-sized tech company may prepare thoroughly before applying, ensuring that all systems align with sustainability goals.
Criteria for achieving ISO 42001 certification
Achieving ISO 42001 certification involves meeting specific criteria, which include:
- Adherence to the documented processes outlined in the ISO 42001 framework.
- Demonstrating continuous improvement in sustainability practices.
- Engaging stakeholders effectively.
Successfully hitting these criteria signals commitment to sustainability, enhancing the organization’s credibility.
Auditing and assessment procedures for ISO 42001
The auditing process for ISO 42001 includes two main types of audits:
- Initial Audit: A thorough examination to assess compliance with the standard.
- Surveillance Audits: Periodic checks to ensure ongoing conformity and improvement.
These procedures allow organizations to identify and address gaps, fostering a culture of accountability and sustainability. Moreover, subsequent audits serve not only as a compliance check but can boost motivation across teams to maintain sustainable practices.

Maintaining and Improving ISO 42001
Continuous improvement practices
Once an organization has achieved ISO 42001 certification, the journey doesn’t end there. Continuous improvement is a cornerstone of effective sustainability management. Organizations should embrace practices such as:
- Regular Review Meetings: Encourage teams to assess ongoing projects and sustainability initiatives.
- Employee Feedback: Solicit input from staff on current practices and areas for improvement.
- Root Cause Analysis: When issues arise, dig deep to understand their origins and address them effectively.
For instance, a retail company might establish regular brainstorming sessions that inspire innovative ideas to lower energy consumption in stores.
Monitoring and measuring performance
To keep sustainability efforts on track, organizations must consistently monitor and measure their performance. Useful strategies include:
- Key Performance Indicators (KPIs): Develop metrics that align with sustainability goals, such as carbon footprint reduction or waste recycling rates.
- Data Collection Tools: Use software solutions to gather and analyze performance data seamlessly.
- Benchmarking: Compare results against industry standards to identify strengths and weaknesses.
Employing these strategies enables organizations to visualize their progress and motivate teams toward shared goals.
Updating and recertification for ISO 42001
As standards and regulations evolve, so must organizations. Updating practices and preparing for recertification is essential. The recertification process typically occurs every three years and involves:
- Review of New Standards: Stay informed about updates in ISO 42001.
- Internal Audits: Conduct self-assessments to ensure compliance before the official audit.
- Documentation Updates: Revise policies and procedures based on performance feedback and new requirements.
By implementing ongoing maintenance strategies, organizations can strengthen their commitment to sustainability and create a culture focused on improvement.

Case Studies and Examples of ISO 42001 Implementation
Real-world examples of successful ISO 42001 implementation
Exploring real-world examples of successful ISO 42001 implementation provides insight into how various organizations navigate the complexities of sustainability. One notable case is that of a manufacturing company in the automotive sector. Upon implementing ISO 42001, they achieved a 20% reduction in energy consumption while simultaneously increasing their operational efficiency. Key strategies included:
- Energy Audits: Conducting thorough assessments to identify waste.
- Employee Training: Upskilling staff on energy-saving methods.
- Sustainable Material Choice: Transitioning to recycled materials in production.
Another compelling example is a multinational food corporation that integrated ISO 42001 into their supply chain. This initiative led to improved stakeholder engagement and a notable 15% decrease in packaging waste, showcasing their commitment to sustainability.
Lessons learned from ISO 42001 case studies
The stories of these organizations yield valuable lessons for others considering ISO 42001:
- Executive Commitment is Key: Successful implementation often starts with strong leadership backing.
- Engagement Across All Levels is Crucial: Involving employees from diverse departments fosters a culture of sustainability.
- Continuous Assessment and Feedback: Organizations must be open to adapting strategies based on performance data and stakeholder input.
These experiences emphasize the need for flexibility and commitment in achieving sustainable practices with ISO 42001, ensuring lasting positive effects on the organization and the environment.

Conclusion and Future Trends
Summary of ISO 42001 benefits
As organizations continue to embrace ISO 42001, the benefits become increasingly evident. The standard not only enhances sustainability but also delivers substantial operational advantages. Key benefits include:
- Increased Efficiency: Streamlining processes often leads to reduced costs and waste.
- Enhanced Reputation: Certification serves as a badge of honor, boosting brand image and stakeholder trust.
- Regulatory Compliance: Staying ahead of environmental regulations minimizes legal risks.
A textile company that adopted ISO 42001 improved its eco-friendliness and attracted more customers by showing real sustainability efforts, leading to increased sales.
Emerging trends in ISO 42001 implementation
Looking towards the future, several trends are shaping the landscape of ISO 42001 implementation:
- Integration with Digital Technologies: Companies are increasingly using data analytics and IoT to monitor sustainability metrics in real time.
- Circular Economy Practices: More organizations are adopting holistic approaches focusing on recycling and reusing materials.
- Collaborative Efforts: Partnerships among businesses, governments, and NGOs are becoming common to amplify the impact of sustainability initiatives.
These trends indicate a promising evolution in how organizations approach sustainability, emphasizing collaboration and innovation. By integrating ISO 42001 into their strategies, companies help create a healthier planet and establish sustainable business models for the modern economy.
For More Information
Check out my AI-generated podcast here: