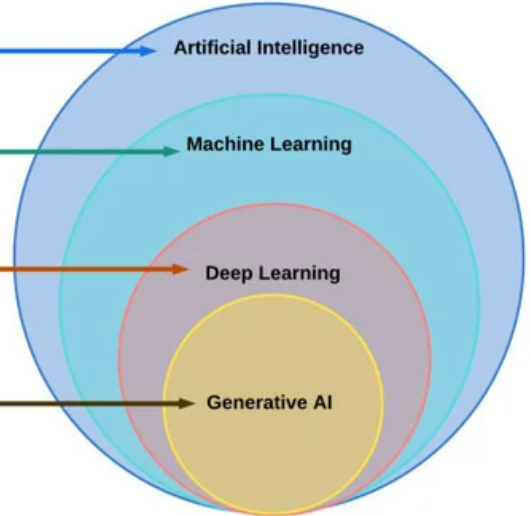
Introduction
Artificial Intelligence (AI), Generative AI, and Machine Learning are three intersecting fields that have gained significant attention in recent years. While they are related, it’s crucial to understand the differences between them.
A brief overview of AI, Generative AI, and Machine Learning
AI refers to the development of computer systems that can perform tasks that typically require human intelligence. This includes problem-solving, decision-making, speech recognition, and more. AI systems are designed to simulate human intelligence and can be further divided into two categories: Narrow AI and General AI. Narrow AI is designed to perform specific tasks, while General AI aims to possess the same capabilities as human intelligence.
Machine Learning is a part of AI that concentrates on algorithms and statistical models that help computers to learn and enhance themselves automatically through experience. It involves training a computer system to recognize patterns in data and make predictions or decisions without explicit programming. Machine Learning algorithms can be supervised, unsupervised, or semi-supervised, depending on the type of input data and the desired outcome.
Generative AI is an advanced type of AI that uses complex algorithms to create new content like images, music, or text that looks like it was made by humans. It utilizes techniques like deep learning and neural networks to analyze large datasets and create original content. Generative AI has applications in various domains, including art, entertainment, and design.
AI is a wide field that includes different technologies. Machine Learning is a part of AI that focuses on algorithms and statistical models. Generative AI is an advanced form of AI that involves creating original content. Understanding these distinctions can help businesses and individuals leverage these technologies effectively.
Understanding AI
Explanation of AI and its applications
Artificial Intelligence (AI) refers to the simulation of human intelligence in machines that can perform tasks typically requiring human intelligence. It involves the development of computer systems capable of analyzing and interpreting data, learning from experience, and adapting to new information. AI has a wide range of applications and is transforming various industries, including healthcare, finance, transportation, and more.
Generative AI is a subset of AI that focuses on creating new content, such as images, videos, or text, based on existing data. It uses algorithms to generate original and creative outputs that mimic human-like qualities. Generative AI has been widely used in areas such as art, design, and entertainment.
Machine Learning is another branch of AI that allows computer systems to automatically learn and improve from experience without being explicitly programmed. It involves the development of algorithms that enable machines to learn patterns from data and make predictions or decisions. Machine Learning has revolutionized areas like data analysis, natural language processing, and robotics.
While Generative AI and Machine Learning are both part of the broader field of AI, they have distinct focuses and applications. Generative AI is primarily concerned with creating new content, while Machine Learning focuses on learning from data to make predictions or decisions. Both have their own unique uses and are contributing to the advancement of AI technology.
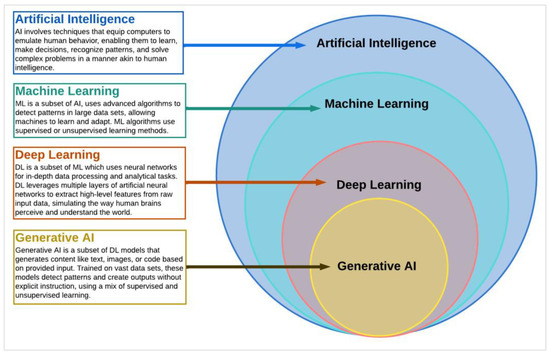
Decoding Generative AI
Insights into Generative AI and its significance
Generative AI refers to a subset of artificial intelligence (AI) that focuses on creating new and unique data, such as images, music, and text. Unlike other branches of AI, such as machine learning, which are primarily focused on analyzing and interpreting existing data, generative AI aims to generate entirely new and original content.
Generative AI relies on generative models, which are trained on big datasets to learn the patterns and structures in the data.These models are then able to generate new content that is similar to the training data but also uniquely different.
Generative AI has significant implications in various industries. For example, in the field of art and design, generative AI can be utilized to create innovative and aesthetically pleasing designs that push the boundaries of traditional design practices. In the music industry, generative AI can help musicians create new melodies and harmonies that they may not have thought of otherwise.
Another important application of generative AI is in the field of content creation. Generative AI algorithms can be used to generate compelling and engaging content, such as articles, blog posts, and social media posts. This can be particularly valuable for businesses that need to produce large amounts of content on a regular basis.
In conclusion, generative AI is a powerful branch of AI that focuses on creating new and unique content. Its ability to generate innovative designs, music, and written content makes it an invaluable tool in various industries.
Unravelling Machine Learning
Exploration of Machine Learning and its importance
Machine Learning (ML) is an important part of Artificial Intelligence (AI). It aims to teach computer systems to learn and make predictions or decisions without being explicitly programmed. It is a subset of AI that uses statistical techniques to allow machines to improve their performance over time.
Machine Learning is crucial in today’s digital era as it powers various applications and technologies that we interact with daily. From search engines and recommendation systems to fraud detection and autonomous vehicles, ML has revolutionized numerous industries.
Machine Learning is important because it can analyze big amounts of data, find patterns and extract valuable insights that can help make informed decisions. By automatically learning from data, ML algorithms can adapt and improve their performance, making them indispensable in addressing complex problems and optimizing processes.
Generative AI systems can create new content, like images, music, or text, without human intervention. They learn from existing data to generate this content. While Machine Learning focuses on making predictions or decisions, Generative AI is about creating new and original content.
In summary, Machine Learning is a vital aspect of AI that empowers computers to learn from data and make predictions or decisions. It plays a pivotal role in various industries and is continuously advancing to tackle complex challenges. Generative AI, on the other hand, is a subset of AI that involves creating new content based on learned models. Both Machine Learning and Generative AI contribute to the advancement of AI technologies and applications.

Key Differences
Comparison between AI, Generative AI, and Machine Learning
Artificial Intelligence (AI), Generative AI, and Machine Learning are all terms that are frequently mentioned in the world of technology. While they are related, there are distinct differences between them.
Artificial Intelligence (AI)
AI refers to the broad field of computer science focused on creating intelligent machines that can perform tasks that typically require human intelligence. AI systems are designed to imitate human cognitive functions such as speech recognition, problem-solving, learning, planning, and decision-making. These systems can analyze vast amounts of data, recognize patterns, and make predictions or recommendations.
Generative AI
Generative AI is a subset of AI that specifically focuses on generating new and original content. It involves using algorithms to create content that mimics human creativity, such as images, music, or text. Generative AI systems learn from existing data and generate new content based on that knowledge. This technology has applications in various industries, including art, design, and entertainment.
Machine Learning
Machine Learning is a subset of AI that focuses on training machines to learn from data and improve their performance without being explicitly programmed. Machine learning algorithms learn and make predictions on their own by being given large amounts of data, instead of specific instructions. They recognize patterns and relationships within the data and adjust their models accordingly. Machine Learning is widely used in areas such as data analysis, image recognition, natural language processing, and recommendation systems.
AI is a broad field that involves creating intelligent machines. Within AI, there are subsets called Generative AI and Machine Learning, each with their own applications and techniques.
Use Cases
Real-world examples of AI, Generative AI, and Machine Learning applications
AI (Artificial Intelligence), generative AI, and machine learning are related concepts that are part of the broader field of computer science and technology. While they share similarities, there are distinct differences between them. Here’s a breakdown of each concept and some real-world examples of their applications.
AI refers to the development of computer systems that can perform tasks that would typically require human intelligence. This includes activities such as problem-solving, speech recognition, decision-making, and image classification. Real-world examples of AI applications include virtual assistants like Siri and Alexa, autonomous vehicles, fraud detection systems, and recommendation engines.
Generative AI, on the other hand, focuses on generating new content or data by learning patterns from existing information. It uses algorithms to create original outputs that mimic human creations. Examples of generative AI applications include art and music generation, text generation, and video game level design.
Machine learning is a subset of AI that involves developing algorithms that can learn and improve from data without being explicitly programmed. It relies on statistical techniques to enable computers to learn and make predictions or decisions. Real-world examples of machine learning applications include spam filtering, personalization algorithms, medical diagnosis systems, and predictive maintenance in industrial settings.
AI includes various tasks that need human-like intelligence. Generative AI creates new content or data, while machine learning uses algorithms to learn and improve from data.These technologies have diverse applications in various industries, revolutionizing the way we live and work.
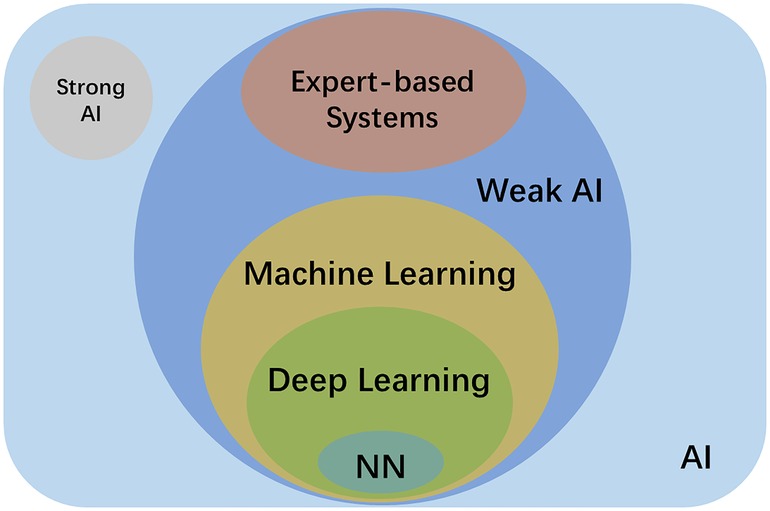
Advancements and Challenges
Discussing the advancements and challenges in the AI field
Artificial Intelligence (AI), Generative AI, and Machine Learning are terms that often get used interchangeably, but they have distinct differences. It is important to understand these differences to grasp the various advancements and challenges in the AI field.
AI
AI refers to the ability of a computer system to perform tasks that would typically require human intelligence. It encompasses a broad spectrum of technologies and applications, including natural language processing, computer vision, and expert systems. AI aims to create systems that can simulate and replicate human intelligence in decision-making, problem-solving, and learning.
Generative AI
Generative AI is a type of AI that focuses on creating new content, like images, music, or text, by using patterns and examples from existing data.It involves using algorithms and models to generate creative outputs that resemble the training data. Generative AI has been used in various fields, including art, design, and music composition.
Machine Learning
Machine Learning is a method of AI that utilizes algorithms and statistical models to enable computers to learn from data and make predictions or decisions without explicit programming. It involves training a model on a dataset and using that model to make predictions or identify patterns in new data. Machine Learning has achieved significant advancements in various domains, including natural language processing, image recognition, and recommendation systems.
While AI, Generative AI, and Machine Learning have all made remarkable progress in recent years, they also face challenges. Some challenges in this field are data privacy and security concerns, ethical issues related to AI algorithms, biases in machine learning models, and the importance of human supervision in critical decision-making.
In conclusion, AI, Generative AI, and Machine Learning are distinct but interconnected fields within the broader scope of artificial intelligence. By understanding these differences and addressing the associated challenges, we can continue to advance these technologies for the benefit of society.
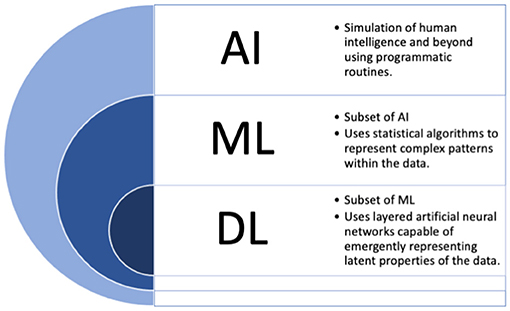
Future Implications
Exploring the potential future implications of AI, Generative AI, and Machine Learning
Artificial Intelligence (AI), Generative AI, and Machine Learning are rapidly advancing technologies that are transforming various industries. While they are often used interchangeably, it is important to understand the distinctions between them and their potential future implications.
AI refers to the simulation of human intelligence in machines that can perform tasks that typically require human intelligence. It involves the development of algorithms and models that enable computers to learn from and make decisions or predictions based on data. The future implications of AI are vast and wide-ranging, from revolutionizing healthcare with personalized medicine to enhancing transportation systems through autonomous vehicles.
Generative AI, on the other hand, focuses on creativity and the generation of new content, such as music, art, or text. It involves training machine learning models to produce original and innovative outputs based on patterns and examples in enormous datasets. The future implications of Generative AI are exciting, as it has the potential to revolutionize industries such as entertainment, design, and advertising, by enabling machines to create unique and compelling content.
Machine Learning is a part of AI that focuses on algorithms and statistical models allowing computers to learn and improve from experience without being explicitly programmed.It involves the development of models that can identify patterns and make predictions or decisions based on large amounts of data. The future implications of Machine Learning are tremendous, as it has the potential to revolutionize numerous industries, including finance, manufacturing, and customer service, by enabling more accurate predictions and improved decision-making processes.
In conclusion, AI, Generative AI, and Machine Learning are transformative technologies with exciting future implications in various industries. Understanding their distinctions and potential applications is essential in harnessing their power to drive innovation and progress.
AI, Generative AI, and Machine Learning: What’s the Difference?
Artificial Intelligence (AI), Generative AI, and Machine Learning are terms often used interchangeably, but they have distinct differences. Understanding these differences can help businesses harness their potential for growth and innovation.
Machine Learning is a part of AI that concentrates on creating algorithms for computer systems to learn and make smart decisions without explicit programming.It is based on the idea that machines can learn from data, identify patterns, and make predictions or decisions.
Generative AI, on the other hand, takes Machine Learning a step further. It involves using machine learning algorithms to generate new, original content. Generative AI models can create new outputs like images, music, and text using existing data, unlike traditional AI models that depend on pre-programmed rules.
The significance of these technologies in today’s world cannot be overstated. AI and Machine Learning are revolutionizing industries by automating tasks, improving efficiency, and enabling data-driven decision-making. Generative AI adds a creative element, allowing businesses to generate unique and personalized content, which can enhance customer experiences and drive innovation.
In conclusion, while AI, Generative AI, and Machine Learning are related, they have distinct differences. Machine Learning focuses on teaching machines to learn from data, while Generative AI goes a step further by creating original content. Understanding these differences can empower businesses to leverage these technologies effectively and stay ahead in the increasingly competitive digital landscape.

Frequently Asked Questions
Common questions and answers related to AI, Generative AI, and Machine Learning
What is AI?
AI, or Artificial Intelligence, refers to the simulation of human intelligence in machines. It involves the development of computer systems that can perform tasks that typically require human intelligence, such as speech recognition, decision-making, and problem-solving.
What is Generative AI?
Generative AI is a subset of AI that focuses on creating new content, such as images, music, or text, that imitates human-like creativity. Generative AI algorithms learn from data and generate new outputs that resemble the patterns and styles in the training data, instead of being explicitly programmed.
What is Machine Learning?
Machine Learning is a method of data analysis that allows computers to learn and make predictions without being explicitly programmed. It involves algorithms that automatically learn and improve from experience by analyzing and finding patterns in large amounts of data.
What’s the difference between AI, Generative AI, and Machine Learning?
While AI is a broad term encompassing different aspects of machine intelligence, Generative AI is a specific branch of AI focused on generating new content. Machine Learning, on the other hand, is a subset of AI that uses mathematical algorithms to learn from data and make predictions.
AI is the idea of simulating human intelligence. Generative AI is responsible for the creation of fresh and original content. Machine Learning allows machines to learn from data and make predictions.