
Overview of Generative AI Adoption in the Workplace
Definition of Generative AI
Generative AI is a class of artificial intelligence systems that can generate new content or data, including text, images, audio, and more. Instead of merely analyzing existing data, generative AI creates unique outputs based on patterns learned from extensive datasets. This technology hinges on sophisticated models such as Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) and Variational Autoencoders (VAEs).
To illustrate, imagine a tool that can compose music or design artwork by inputting simple keywords. This capability transforms the creative process, allowing individuals and organizations to explore new ideas with less manual effort.
Significance of Generative AI in Business Settings
Adopting generative AI in business settings is not just a trend; it is a transformative approach redefining how companies operate. Some key aspects of its significance include:
- Enhanced Creativity: Generative AI enables teams to brainstorm and create innovative marketing materials or product designs, pushing the boundaries of creativity.
- Cost Efficiency: By automating routine creative tasks, organizations can save time and resources, allowing human talent to focus on strategic planning and analysis.
- Better Decision-Making: With data-driven insights generated from AI, businesses can make more informed decisions swiftly.
In summary, the integration of generative AI presents an exciting opportunity for companies to enhance creativity, streamline processes, and gain a competitive edge in their respective markets.

Benefits of Using Generative AI at Work
Enhanced Creativity and Innovation
One of the most exciting benefits of incorporating generative AI into the workplace is the boost in creativity and innovation. For instance, consider a marketing team tasked with developing a campaign. With generative AI, team members can input ideas into the system and receive various creative suggestions, ranging from taglines to graphic designs. This collaboration between human intuition and machine-generated options opens avenues for unprecedented creativity.
Increased Productivity and Efficiency
Generative AI significantly enhances productivity by automating mundane tasks. For example:
- Automated Reports: AI can quickly generate in-depth reports by processing large data sets, freeing up analysts to focus on strategy.
- Drafting Documents: With tools that generate text based on templates or keywords, employees can drastically reduce the time spent on document creation.
By streamlining workflows, teams can allocate more time to higher-level strategic initiatives.
Personalized Customer Interactions
Another notable benefit is the ability to enhance customer interactions. For instance, AI can analyze customer data and generate tailored recommendations, making customers feel valued and understood.
Examples include:
- Chatbots: Offering personalized responses that address specific queries based on a user's previous interactions.
- Content Creation: Generating custom emails or promotional materials that resonate with individual customer preferences.
In essence, generative AI equips organizations with the tools to foster creativity, drive productivity, and personalize the user experience, paving the way for business growth and enhanced satisfaction.

Challenges and Limitations of Implementing Generative AI
As organizations increasingly recognize the benefits of generative AI, they must also navigate several challenges with its implementation. Addressing these challenges is vital for ensuring a successful transition to AI-enhanced workflows.
Data Privacy and Security Concerns
One of the foremost challenges is data privacy and security. Generative AI often relies on vast datasets, including sensitive customer information. Companies must comply with GDPR and HIPAA regulations to safeguard data. For example, a breach of sensitive information can lead to severe reputational damage and financial penalties. Key measures to consider include:
- Data Anonymization: Removing personally identifiable information from datasets.
- Robust Security Protocols: Implementing encryption and access controls to protect data integrity.
Algorithm Bias and Fairness
Another critical challenge is the issue of algorithm bias. Generative AI can inadvertently perpetuate existing biases in datasets, leading to unfair outcomes. For instance, if a marketing AI system is trained on biased consumer data, it may create ads that do not resonate with diverse populations. To mitigate these issues:
- Diverse Training Datasets: Ensure data sources reflect a broad range of demographics.
- Regular Audits: Continuously monitor algorithms for fairness and adjust training as needed.
Integration with Existing Systems
Lastly, integrating generative AI with existing systems can pose technical challenges. Many organizations still rely on legacy systems that may not be compatible with advanced AI tools. Companies should consider:
- Incremental Implementation: Start with pilot projects to assess compatibility before a full rollout.
- Cross-Functional Teams: Form teams that include IT, data science, and business units for a cohesive integration strategy.
Navigating these challenges is essential for organizations to fully leverage the potential of generative AI while maintaining ethical and operational integrity.
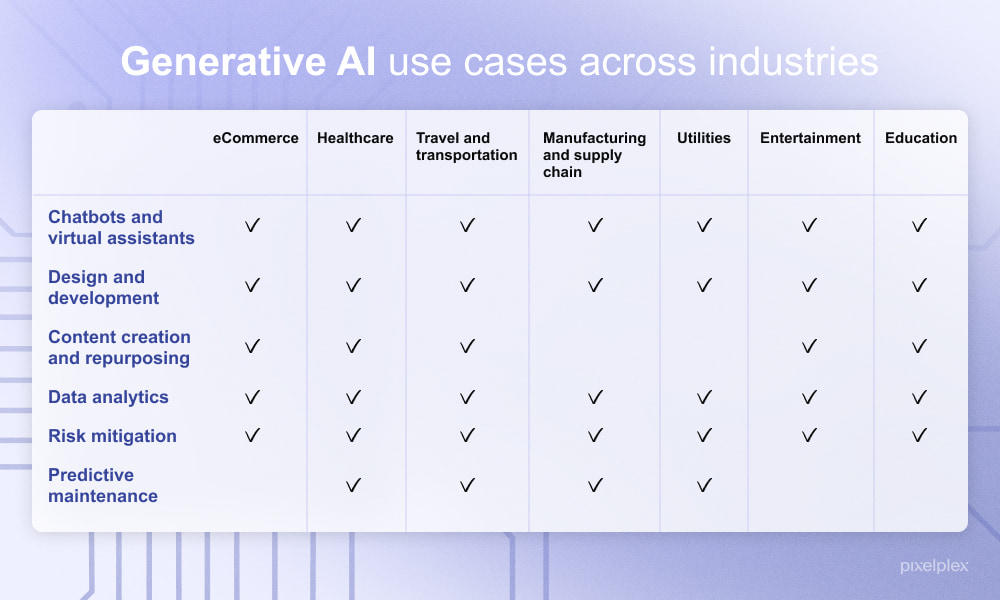
Use Cases of Generative AI in Different Industries
Despite the challenges and limitations, generative AI is making significant strides across various industries, reshaping how businesses operate. Understanding its specific applications can provide insight into its transformative potential.
Marketing and Advertising
In the marketing and advertising sector, generative AI has become a game-changer. Companies can now automate personalised content creation, from social media posts to email campaigns. For example, an AI system can analyze a customer’s behavior and preferences to generate tailored advertisements that resonate deeply. Key benefits in this domain include:
- Dynamic Content Creation: Adaptive advertisements that change based on real-time data.
- Enhanced Targeting: Improved segmentation of customer bases, increasing conversion rates.
Healthcare
The healthcare industry is also experiencing significant innovations powered by generative AI. AI algorithms can assist in generating synthetic medical data that helps in training other AI models without compromising patient confidentiality. Additionally:
- Drug Discovery: Generative AI can predict molecular behavior, speeding up the development of new treatments.
- Personalized Medicine: Tailoring treatment plans based on individual patient data enhances healthcare outcomes.
Finance
In finance, generative AI plays a vital role in risk assessment and fraud detection. By analyzing vast amounts of transaction data, AI can identify unusual patterns indicative of fraudulent activity. Noteworthy applications include:
- Automated Report Generation: AI generates complex financial reports efficiently.
- Customer Service Automation: Chatbots powered by generative AI offer real-time support, answering queries and providing financial advice.
In summary, generative AI is revolutionizing marketing, healthcare, and finance industries, demonstrating its capacity to drive innovation and efficiency. Each of these use cases showcases how AI technology can lead to improved processes and enhanced experiences for customers and stakeholders alike.
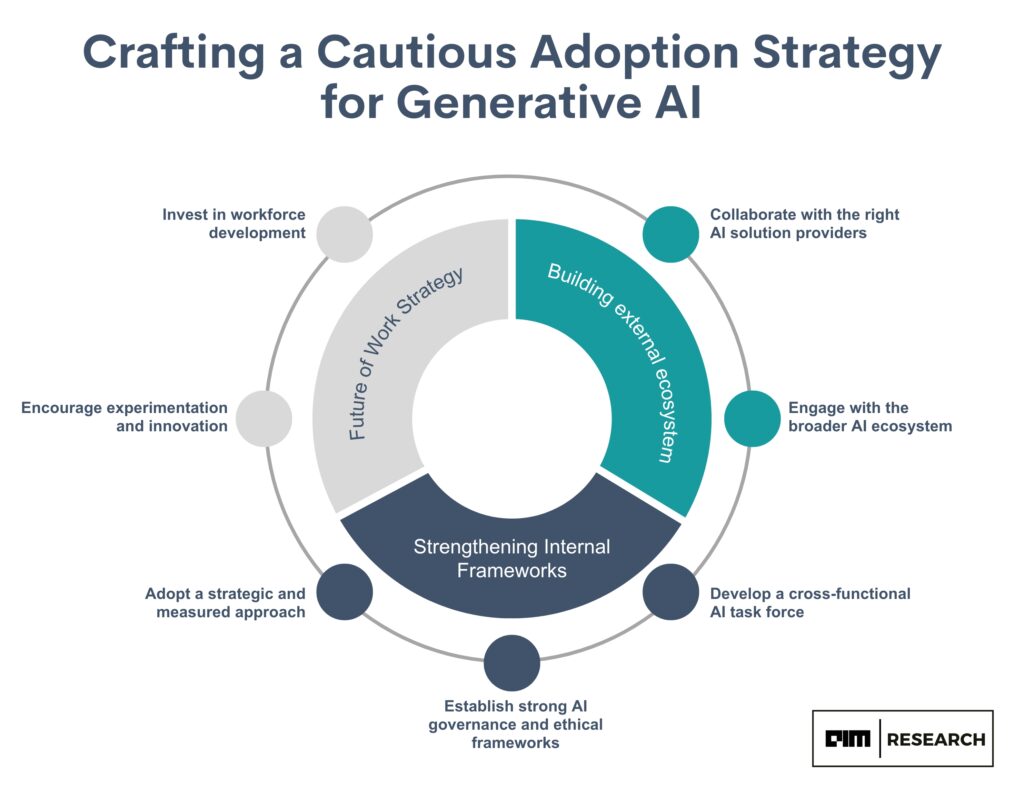
Strategies for Successful Integration of Generative AI
Organizations must adopt comprehensive strategies for its integration to maximise the benefits of generative AI. Companies can navigate the complexities of AI adoption by focusing on key areas such as employee training, collaboration, and ethical considerations.
Employee Training and Education
One of the foundational strategies is investing in employee training and education. Ensuring that team members understand how to use generative AI tools effectively is vital. Consider the following approaches:
- Workshops and Seminars: Conduct regular sessions to educate employees about the capabilities and limitations of generative AI.
- Hands-on Training: Provide opportunities for employees to practice with AI tools in a supportive environment, encouraging experimentation.
For example, a company that rolled out a new AI-powered design tool ran workshops where employees could create marketing materials, enhancing their skills and confidence.
Collaborative Work Environment
Fostering a collaborative work environment is equally important. Generative AI thrives in settings where diverse perspectives come together. Encourage cross-functional teams to collaborate on AI projects, combining insights from:
- Marketing: Understanding customer behavior and preferences.
- IT: Addressing technical challenges and ensuring smooth integration.
The synergy of varied expertise can lead to innovative AI solutions that cater to organizational needs.
Ethical Guidelines and Governance
Lastly, establishing ethical guidelines and governance is crucial in managing the implications of generative AI. Organizations should develop frameworks that outline best practices for:
- Data Usage: Ensuring compliance with data protection regulations.
- Bias Mitigation: Implementing strategies to minimize algorithm bias.
By prioritizing ethical considerations, companies can build trust with stakeholders and mitigate risks associated with AI deployment. Collectively, these strategies create a solid foundation for effectively integrating generative AI, paving the way for sustained growth and success in the digital age.
Future Trends and Developments in Generative AI
As organizations continue to adopt generative AI, several future trends and developments are poised to reshape the landscape, influencing how businesses operate and thrive in an increasingly digital world.
Advancements in Natural Language Processing
Natural Language Processing (NLP) is one of the most exciting areas where generative AI is making significant strides. The development of more sophisticated language models enables machines to understand and generate human-like text with greater accuracy. For example, contextual understanding is improving, allowing AI to engage in more meaningful conversations. This opens doors to applications such as:
- Intelligent Chatbots: Providing customer support that feels conversational and intuitive.
- Content Creation: Generating articles, reports, and even poetry that resonate with human emotions.
Evolution of Generative AI Tools
The tools surrounding generative AI are also evolving rapidly. New emerging platforms make it easier for businesses to harness AI capabilities without requiring deep technical expertise. Expect to see:
- User-Friendly Interfaces: Simplified tools enable users to create content without coding skills.
- Integration Capabilities: AI tools that easily connect with existing software applications, enhancing workflows.
This democratization of AI technology means that more organizations can utilize its benefits.
Impact on Job Roles and Skills
Finally, generative AI will significantly impact job roles and required skills as it continues to evolve. While some fear job displacement, others see opportunities for new roles that leverage AI. For instance:
- AI Trainers: Professionals who train AI models to reduce bias and improve outputs.
- Data Curators: Individuals responsible for managing and preparing data for AI systems.
Overall, reskilling and upskilling will become essential as job descriptions shift to accommodate the rise of generative AI. In embracing these future trends, organizations can better prepare their workforce and stay ahead in the competitive innovation landscape.

Conclusion
As we reflect on the evolving landscape of generative AI, it's crucial to acknowledge the myriad benefits it brings to organizations.
Recap of Generative AI Benefits
Generative AI is not just a technological marvel; it’s a powerful tool that enhances creativity, boosts productivity, and fosters personalized customer experiences. Organizations leveraging this technology have reported:
- Increased Efficiency: Employees can focus more on strategic initiatives by automating routine tasks.
- Enhanced Creativity: AI-generated insights inspire innovative solutions that might not have been considered otherwise.
- Improved Customer Relationships: Tailored interactions create a more engaging customer experience, increasing satisfaction and loyalty.
For instance, a content marketing agency using generative AI tools to develop custom campaigns described how it revolutionized their creative process, saving them countless hours.
Implications for Future Workplace Dynamics
Looking ahead, the implications of generative AI for workplace dynamics are profound. As AI continues integrating into everyday operations, roles will adapt and shift towards collaboration with technology.
Consider the rise of hybrid teams where humans and AI work side-by-side, leading to:
- Cross-Disciplinary Roles: New positions focusing on AI oversight, ethical governance, and data management will emerge.
- Continuous Learning Environment: Ongoing education and training will be vital as the workforce adapts to AI capabilities.
In conclusion, generative AI enhances operational efficiency and transforms workplace dynamics, paving the way for a more innovative, collaborative, and agile future. Embracing these changes will position organizations at the forefront of their industries, ready to tackle the challenges and embrace the opportunities ahead.




