Introduction
Importance of Identity and Access Management
In today’s digital landscape, the significance of Identity and Access Management (IAM) cannot be overstated. As organizations increasingly rely on technology, ensuring the right individuals have appropriate access to resources is crucial. IAM not only helps mitigate security risks but also enhances organizational efficiency. Consider a scenario where an employee leaves their position without revoking access to sensitive company data. This oversight can lead to unauthorized access and potential breaches. Therefore, implementing a robust IAM strategy is vital for protecting critical assets.
Overview of Data and Privacy Protection
With the rise of data breaches, understanding data and privacy protection has become essential for organizations of all sizes. Here are a few key components to consider:
- Data Encryption: Protect sensitive information by converting it into an unreadable format, ensuring only authorized users can access it.
- Access Controls: Establish rules that define who can view or modify data.
- Regular Audits: Conduct assessments to identify vulnerabilities and ensure compliance with security policies.
Businesses can cultivate trust and safeguard their stakeholders’ personal information by prioritising these elements.
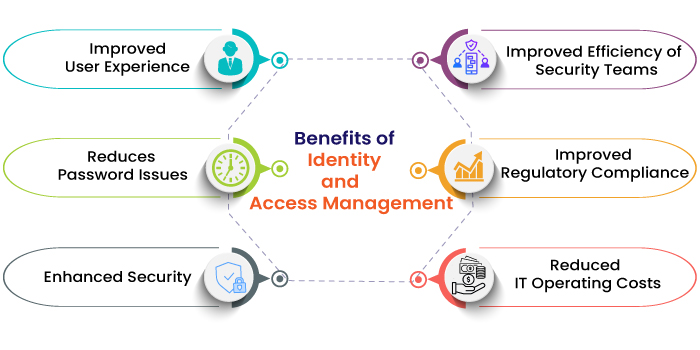
Understanding Identity Management
Definition and Purpose
Identity Management refers to organisations’ processes, policies, and technologies to identify, authenticate, and authorize individuals accessing their systems. It’s about ensuring people access the right resources at the right time. For instance, imagine a healthcare facility where patient records are accessed by various personnel; effective identity management helps ensure that only authorized doctors and nurses view sensitive information, safeguarding patient privacy.
Benefits of Effective Identity Management
The advantages of implementing an effective identity management framework are numerous:
- Enhanced Security: Reducing the risk of unauthorized access and data breaches.
- Improved Compliance: Adhering to regulations like GDPR, which mandates specific controls over personal data.
- Operational Efficiency: Streamlining user access processes, which, in turn, minimizes downtime.
- User Satisfaction: Providing seamless access for users through Single Sign-On (SSO) makes their experience smoother.
Adopting identity management practices secures sensitive information and fosters a culture of trust and accountability within the organization.
Role of Access Management
Types of Access Control
Access Management safeguards an organization’s digital assets by regulating who can access what. Various types of access control methods can be utilized, depending on the specific needs and security requirements:
- Discretionary Access Control (DAC): Resource owners can determine who has access. Think about a project manager granting team members access to a project folder.
- Mandatory Access Control (MAC): Access rights are assigned based on regulations in this rigid framework. Government facilities often employ this to protect sensitive information.
- Role-Based Access Control (RBAC): Access is granted based on a user’s role within the organization. For example, an accountant will have different access rights than someone in IT.
Implementing Access Management Solutions
Successfully implementing access management solutions requires careful planning and execution. Here’s how organizations can approach it:
- Identify Resources: Determine what data and systems need protection.
- Define User Roles: Categorize users based on their activities and responsibilities.
- Choose the Right Tools: Identity Governance and Administration (IGA) or Access Management Systems.
- Regularly Review Access: Conduct audits to ensure that access permissions remain relevant.
Organizations can create a secure environment that minimizes risk while enhancing productivity by developing a robust access management strategy.

Best Practices for Data Protection
Data Encryption
Implementing robust data protection practices is essential as organizations increasingly rely on digital data. One of the most effective techniques is data encryption. This process transforms readable information into an unreadable format, ensuring only authorized personnel can access it. For example, consider a financial institution storing sensitive client information. By encrypting data, even if a cybercriminal gains access to their systems, the stolen data will be useless without the appropriate decryption key. Here are a few key points about data encryption:
- End-to-End Encryption: Secures data from the source to its destination, preventing interception during transmission.
- Full Disk Encryption: Protects an entire storage medium, rendering data inaccessible without proper authentication.
- Regular Key Management: Ensures encryption keys are securely generated, distributed, and rotated.
Regular Security Audits
Another crucial aspect of data protection is conducting regular security audits. These evaluations help organizations identify vulnerabilities and ensure compliance with internal policies and regulatory standards. Consider making audits part of your routine with the following practices:
- Schedule Periodic Reviews: Conduct audits quarterly or bi-annually to stay ahead of potential threats.
- Involve a Third Party: Bringing in external experts can provide an unbiased view of your security posture.
- Document Findings: Keep a detailed record of vulnerabilities identified and actions taken to resolve them.
Organizations can create a robust framework for securing sensitive information by combining data encryption with regular security audits.

Compliance with Regulations
GDPR and Identity Management
Navigating the identity management landscape requires a keen understanding of compliance regulations, particularly the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR). This regulation, which came into effect in May 2018, is designed to protect the personal data of European Union citizens. This means organisations must implement strong identity management practices to ensure compliance. Here are a few critical points regarding GDPR and identity management:
- Data Minimization: Collect only the data necessary for specific purposes.
- User Consent: Ensure data subjects provide explicit consent before collecting their information.
- Right to Access: Grant individuals the ability to access and request deletion of their personal data.
Adopting these principles helps in compliance and builds trust with consumers.
Impact of CCPA on Privacy Protection
Similarly, the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) has significantly influenced how organizations handle personal data. Effective January 2020, this regulation grants California residents enhanced privacy rights, including:
- The Right to Know: Consumers can request details on the personal data collected about them.
- The Right to Opt-Out: Individuals can opt out of selling their personal information.
Organizations must proactively adapt their identity management frameworks to accommodate these rights. By focusing on robust compliance with regulations like GDPR and CCPA, companies can ensure privacy protection while fostering an environment of accountability and trust.

Emerging Technologies in IAM
Biometric Authentication
As the demand for secure identity management increases, emerging technologies like biometric authentication are gaining traction. This method uses unique physiological characteristics—such as fingerprints, facial recognition, or iris patterns—to verify users’ identities. Imagine entering a secure facility and scanning your fingerprint at the entrance. This seamless experience not only enhances security but also improves user convenience. Here are some key advantages of biometric authentication:
- Increased Security: Unlike passwords, biological traits are difficult to replicate or steal.
- User Convenience: Quick access eliminates the need to remember complex passwords.
- Reduced Fraud: Biometric systems are less susceptible to fraud than traditional methods.
Artificial Intelligence in Access Control
Another game-changing technology is Artificial Intelligence (AI), which enhances access control mechanisms. By analyzing vast amounts of data, AI can swiftly adapt access policies based on user behavior patterns. Consider a scenario where an employee attempts to access sensitive data outside usual hours; AI systems can flag this as suspicious and trigger additional security protocols. Key benefits of implementing AI in access control include:
- Real-Time Analytics: Instant insights into user behavior help preempt security breaches.
- Adaptive Security Measures: Access policies can evolve automatically to meet changing risk profiles.
- User Context Awareness: AI can evaluate the context in which access is requested, adding an additional layer of security.
By integrating biometric authentication and AI solutions in Identity and Access Management, organizations can strengthen their security frameworks and enhance user experience.
Challenges and Solutions
Identity Theft Risks
In the rapidly evolving digital landscape, identity theft remains a significant concern for individuals and organizations. Cybercriminals constantly devise sophisticated methods to steal personal information, often leading to severe financial and reputational damage. Consider a case where hackers gained unauthorized access to an organization’s database and compromised sensitive employee information. Such breaches can have disastrous consequences, including loss of trust and hefty legal repercussions. Key challenges in combating identity theft include:
- Phishing Attacks: Deceptive emails trick individuals into revealing sensitive information.
- Weak Password Practices: Many users still favor simple and easily guessable passwords.
- Social Engineering: Manipulating individuals into divulging confidential information.
Multi-Factor Authentication
An effective solution to mitigate identity theft risks is the implementation of Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA). This security measure requires users to provide two or more verification factors when accessing sensitive information. Benefits of MFA include:
- Enhanced Security: Even if a password is compromised, an additional verification step, like a fingerprint or a one-time code, is needed for access.
- User Accountability: MFA helps track user activity more effectively, enhancing the ability to detect suspicious behavior.
- Reduced Risk of Breaches: With multiple layers of security, the likelihood of unauthorized access greatly diminishes.
By addressing identity theft risks through proactive measures such as multi-factor authentication, organizations can protect their valuable assets and foster a culture of security awareness.
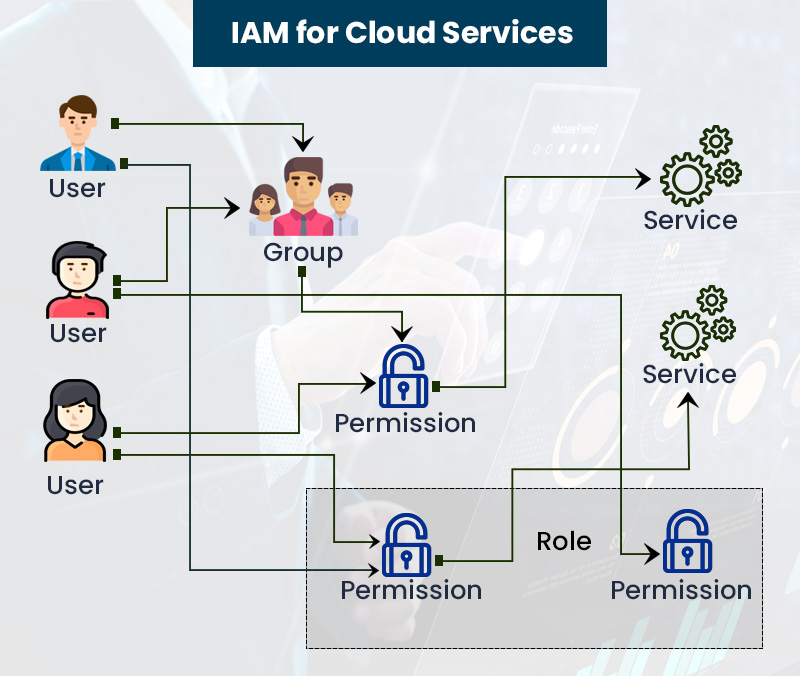
IAM in the Cloud Environment
Cloud-Based Identity Solutions
As organizations increasingly migrate to the cloud, the significance of Identity Access Management (IAM) in this environment cannot be underestimated. Cloud-based identity solutions offer flexibility and scalability that traditional on-premises systems can’t match. Imagine a company expanding its workforce globally; with cloud-based IAM, user identities and access rights can be managed anywhere. Key advantages of these solutions include:
- Scalability: Easily adjust user access as the organization grows without the need for significant infrastructure changes.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Reduced hardware expenses and maintenance as cloud providers handle the heavy lifting.
- Enhanced Collaboration: Employees can securely access necessary applications and data regardless of location.
Securing Remote Access
However, with the growth of remote work, securing access to cloud resources becomes critical. Implementing strategies for securing remote access ensures sensitive information remains protected. Here are some effective practices:
- VPN Usage: Encourage employees to utilize Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) for encrypted connections to the organization’s network.
- Reinforce MFA: As discussed earlier, requiring multiple authentication factors further secures remote access.
- Endpoint Security: Ensure that devices accessing the network have up-to-date security software to fend off potential threats.
By embracing cloud-based identity solutions and implementing stringent remote access security measures, organizations can confidently protect their data while fostering a flexible and productive work environment.

Case Studies in IAM Implementation
Successful IAM Strategies
Examining real-world Identity and Access Management (IAM) applications can offer invaluable insights into effective strategies. One notable example is a major financial institution that revamped its IAM framework by integrating biometric authentication alongside traditional methods. This organization experienced a significant reduction in unauthorized access attempts and enhanced customer trust. Key components of their successful strategy included:
- User-Centered Design: Focusing on the user experience helped drive higher adoption rates of the new system.
- Ongoing Training: Regular training sessions ensured employees stayed updated on best practices.
- Robust Monitoring: Continuous monitoring allowed for rapid identification of anomalies.
Lessons Learned from IAM Failures
Conversely, exploring IAM failures provides crucial lessons. For instance, a large retail chain faced a massive data breach due to inadequate access controls. Despite possessing a wealth of customer data, the company lacked multi-factor authentication, ultimately leading to expensive consequences. Some key lessons from this failure include:
- Prioritize Access Control Policies: Without effective policies, risks increase exponentially.
- Conduct Regular Security Audits: Routine evaluations can catch vulnerabilities before exploiting them.
- Invest in Employee Awareness: Ensuring employees understand the importance of security practices is vital.
Organizations can enhance their strategies and better protect sensitive information by analysing successes and failures in IAM implementation.