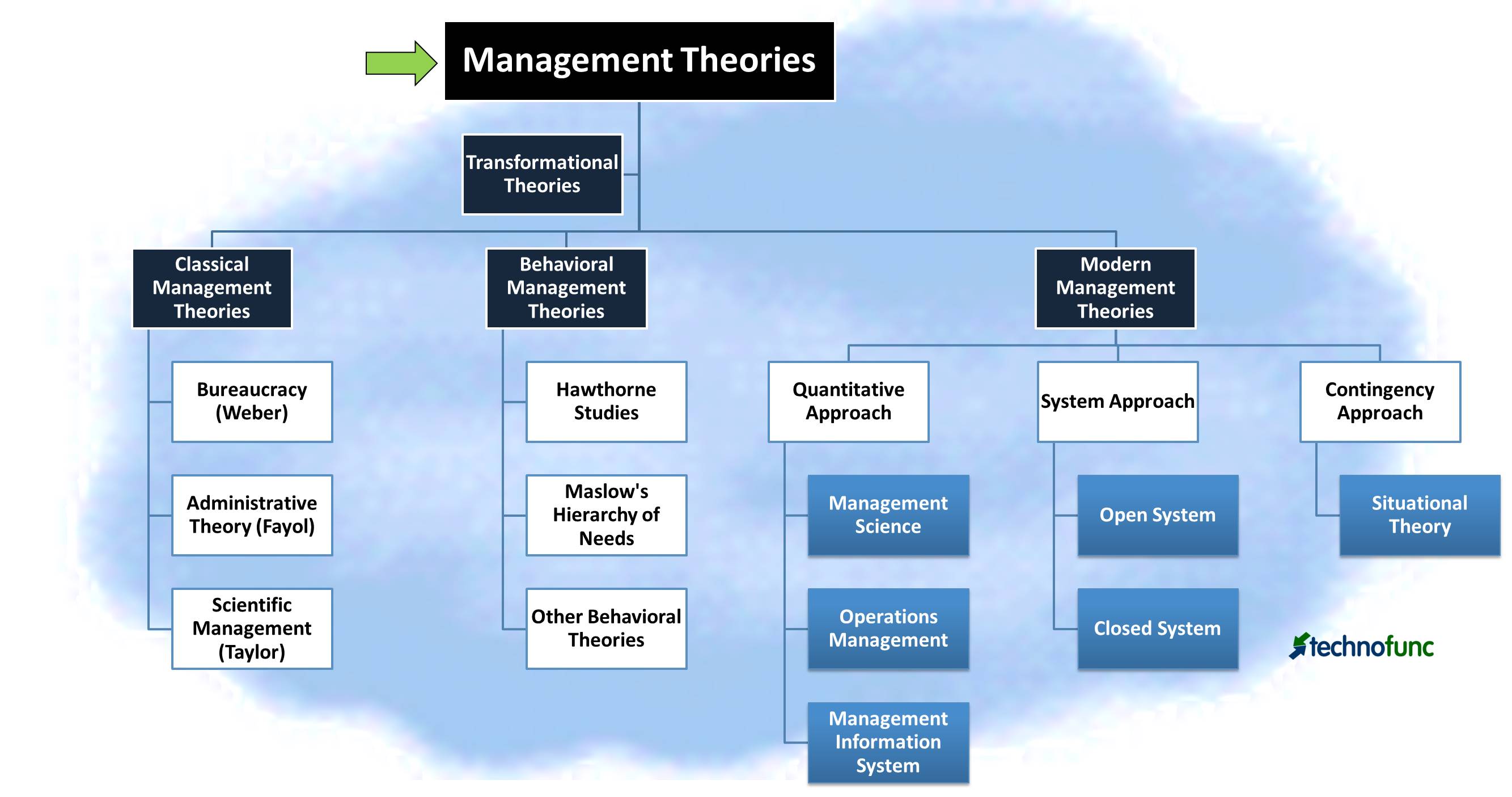
Organization management is the process of planning, organizing, and controlling resources to achieve specific goals. Over time, management theories have developed to help businesses and organizations achieve these goals more efficiently. In this guide, we will discuss some of the most important management theories and how they are used in organizations.
Scientific Management Theory:
Scientific management theory is one of the earliest management theories and was developed by Frederick Winslow Taylor in the 1900s. This theory suggests that every job can be broken down into smaller tasks, and managers should focus on optimizing each task to increase overall efficiency. The theory also emphasizes selecting and training employees based on their abilities to perform specific tasks.
This theory is still relevant today and is used in organizations that require high levels of precision and efficiency in their operations. For example, factories and assembly lines use this theory to optimize their production processes.
Human Relations Theory:
The Human Relations Theory suggests that a worker’s productivity is influenced by social, psychological, and emotional factors. This theory emerged in the 1930s, with Elton Mayo being one of its key figures. According to this theory, workers will be more productive when they feel like they are part of a team and are treated with respect and dignity.
Organizations use this theory to ensure that their employees are satisfied with their jobs, which can lead to improved productivity, motivation, and job satisfaction. This theory is relevant in organizations where employees perform tasks that require teamwork and collaboration, such as healthcare teams or software development teams.
Management by Objectives (MBO):
The Management by Objectives (MBO) theory was developed by Peter Drucker in the 1950s. This theory emphasizes setting specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) objectives for employees. Managers and employees work together to set these objectives and develop a plan to achieve them.
MBO is used in organizations to align employee goals with the organization’s objectives. This can lead to increased employee motivation and job satisfaction, as they feel they are contributing to the organization’s success. This theory is relevant in organizations where employees work in a results-oriented environment, such as sales teams or marketing teams.
Contingency Theory:
Organizations use this theory to adapt their management style to different situations and contexts. For example, a leader who is authoritarian and directive may be more effective in a crisis, but a leader who is collaborative and participative may be more effective in a stable environment. This theory is relevant in organizations that operate in different contexts or are facing a rapidly changing environment.
The Contingency Theory suggests that there is no one-size-fits-all approach to management and that the style of management should be based on the situation. This theory was developed by Fred Fiedler in the 1960s and proposes that the effectiveness of a leader depends on the interaction between the leader’s style and the characteristics of the situation.
Conclusion:
Management theories provide a framework for organizations to optimize their operations, increase productivity, and achieve their goals efficiently. The scientific management theory emphasizes efficiency and precision, while the human relations theory emphasizes employee satisfaction and motivation. Management by Objectives aligns employee goals with organizational objectives, and the contingency theory emphasizes the importance of adapting management style to the situation. Ultimately, understanding and applying these theories can help organizations succeed and thrive.