Welcome to our second blog post on organisational behaviour theories! This detailed article will explore the evolution and various schools of thought in organisational behaviour theories. Understanding these theories can help us understand how people and groups behave in an organization, and how their behavior affects the organization’s success.
Evolution of Organisational Behaviour Theories
Organisational behaviour theories have evolved significantly over time, influenced by various factors. This section will delve into the historical development of these theories and shed light on the factors that have driven their evolution.
Theories of organizational behavior started in the early 20th century when management became more interested in understanding and managing people in organizations, instead of just focusing on productivity.The industrial revolution and advancements in psychology and sociology greatly influenced the development of these theories.
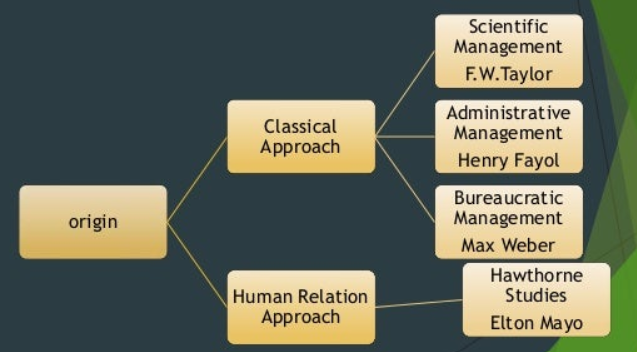
The classical organisational behaviour theories emerged during the early 1900s, with prominent theorists such as Frederick Taylor and Henri Fayol. These theories emphasised scientific management, division of labour, hierarchy, and bureaucracy. They aimed to improve efficiency and productivity in the workplace.
However, as the workplace became more complex and dynamic, the limitations of classical theories became evident. This led to contingency theories, which recognise that there is no universal approach to managing organisations. Instead, these theories propose that the best course of action depends on various situational factors, such as industry, organisational culture, and technology.
Behavioural, organisational behaviour theories evolved in the mid-20th century, with theorists such as Douglas McGregor and Abraham Maslow. These theories shifted the focus to the individual within the organisation, highlighting the importance of motivation, job satisfaction, and human needs. They emphasised the role of leadership, employee participation, and recognition in achieving organisational goals.
In recent years, modern organisational behaviour theories have emerged to address the challenges organisations face in the ever-changing business landscape. These theories consider factors such as globalisation, technological advancements, and increasing diversity in the workplace. They explore concepts like emotional intelligence, organisational culture, and innovation to understand and manage the complexities of modern organisations.
Organizational behavior theories have evolved to meet the changing needs of organizations. These theories aim to improve performance, engage employees, and adapt to the changing business environment.
Classical Organisational Behaviour Theories
Classical organisational behaviour theories originated during the early 20th century and laid the foundation for understanding how organisations function, and individuals behave within them.
Critical Principles of Classical Organisational Behaviour Theories
- Scientific Management: Developed by Frederick Taylor, this theory focuses on systematically studying work processes to increase efficiency and productivity. It emphasises the division of labour, standardisation, and scientific methods to eliminate inefficiencies.
- Bureaucratic Theory: Proposed by Max Weber, this theory highlights the importance of a hierarchical structure, well-defined roles and responsibilities, and adherence to rules and procedures in achieving organisational goals. It emphasises rationality, impersonality, and separating personal and official functions.
- Administrative Theory: Developed by Henri Fayol, this theory focuses on the managerial functions of planning, organising, commanding, coordinating, and controlling. It emphasises clear communication, effective leadership, and proper coordination to ensure organisational success.
Despite being developed over a century ago, classical organisational behaviour theories remain relevant in the modern workplace. The principles of scientific management are utilised in process-driven industries to improve efficiency and quality. The bureaucratic approach provides a framework for formal organisations to maintain structure and control. The administrative process helps managers effectively oversee and coordinate tasks within their teams.
Contingency Organisational Behaviour Theories
Contingency theories propose no one-size-fits-all approach to understanding and managing organisational behaviour. Instead, these theories suggest that the effectiveness of different corporate behaviour strategies depends on the specific circumstances and context in which they are applied.
The situational contingency theory states that the most effective strategies for organizational behavior rely on the specific characteristics of the organization and its environment.
Another notable contingency theory is the path-goal theory, which focuses on the leader’s role in motivating employees to achieve their goals. According to this theory, leaders should adopt different behaviours depending on the characteristics of the employees and the nature of the task at hand.
While contingency theories have significantly contributed to understanding the relationship between organisational behaviour and environmental factors, they also have limitations. One limitation is that they may oversimplify complex organisational behaviour by focusing on a limited number of variables. Additionally, contingency theories may only partially explain the dynamic nature of organisational behaviour, which can change over time.
Behavioural Organisational Behaviour Theories
Behavioural organisational behaviour theories focus on the human aspects of an organisation and how they impact individual and group behaviour within the workplace. These theories emphasise understanding the psychology and motivations of employees and how they influence their job performance and satisfaction.
Key Concepts and Principles
One of the key concepts in behavioural and organisational behaviour theories is that individuals are motivated by various factors, including their needs, desires, and aspirations. These theories also highlight the importance of feedback and reinforcement in shaping employee behaviour. Additionally, behavioural theories emphasise the role of leadership in influencing employee attitudes and behaviours.
Another principle in behavioural, organisational behaviour theories is that employees’ decision-making is influenced by their cognitive processes and perceptions. These theories suggest that individuals interpret and make sense of their work environment based on their unique beliefs, values, and experiences.
Furthermore, behavioural theories emphasise the importance of social interactions within the workplace and how they shape employee behaviour. These theories highlight the significance of communication, teamwork, and collaboration in fostering positive workplace relationships and enhancing organisational performance.
Contribution to Employee Motivation and Job Satisfaction
Behavioural organisational behaviour theories provide valuable insights into understanding and enhancing employee motivation and job satisfaction. Orgrecognisingcan design motivational strategies that cater to individual needs and drive job satisfaction by recognising the diverse factors that influence employee behaviour.
These theories also highlight the significance of providing employees with constructive feedback and recognition for their efforts, enhancing their motivation and job satisfaction. Additionally, behavioural approaches stress the importance of creating a positive work environment that fosters social support and teamwork, contributing to higher employee satisfaction and motivation.
Behavioural organisational behaviour theories provide a good understanding of how people behave in organizations. They also help guide managers in motivating employees and making them more satisfied with their jobs, which can lead to better performance.
Modern Organisational Behaviour Theories
In recent years, new theories have emerged in organisational behaviour, offering fresh perspectives and insights into understanding human behaviour within the workplace. These modern theories focus on addressing contemporary challenges organisations face, such as increasing diversity, globalisation, and technological advancements. Here are some of the critical current organisational behaviour theories:
1. Social Identity Theory
Social identity theory explores how individuals’ sense of self and group membership influence their behaviour within an organisational context. This theory emphasises the importance of identity, belongingness, and social categorisation in shaping employee attitudes, motivation, and performance.
2. Mental Models Theory
Mental models theory suggests that individuals develop cognitive frameworks or mental models to understand and interpret their environment. These mental models influence how individuals perceive and interact with their work environment, leading to varying behaviours and decisions. Understanding employees’ mental models can help organisations identify potential barriers and facilitate effective communication and collaboration.
3. Emotional Intelligence Theory
Emotional intelligence theory focuses on individuals’ ability to recognise, understand, and manage their emotions and the emotions of others. This theory highlights the importance of emotional awareness and emotional regulation in the workplace, as it influences employee engagement, teamwork, and decision-making.
4. Positive Organisational Scholarship
Positive Organisational Scholarship (POS) focuses on identifying and understanding factors contributing to positive organisational outcomes, such as employee well-being, flourishing, and engagement. POS theories emphasise the importance of strengths, positive emotions, and positive relationships in enhancing organisational performance and creating a thriving work environment.
5. Systems Theory
Systems theory views organisations as complex systems composed of interconnected parts that influence each other and the organisation’s overall functioning. This theory highlights the importance of seeing the organization as a whole. It acknowledges that different parts of the organization, like individuals, teams, departments, and the external environment, are connected and affect each other.
These modern organisational behaviour theories offer valuable insights for organisations seeking to understand and manage the complexities of the contemporary workplace. By applying these theories, organisations can enhance employee well-being, productivity, and adaptability, ultimately contributing to long-term success.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the study of organisational behaviour theories has evolved, influenced by various factors such as societal changes, technological advancements, and modern workplace needs. Classical organisational behaviour theories laid the foundation for understanding organisational structures and management practices, while contingency theories highlighted the importance of adapting to environmental factors. Behavioural approaches emphasise the significance of employee motivation and job satisfaction.
Modern organisational behaviour theories have emerged to address contemporary workplace challenges such as diversity, globalisation, and changing employee expectations in recent years. These theories aim to enhance organisational effectiveness, foster innovation, and promote employee well-being.
Overall, studying organisational behaviour theories provides valuable insights for managers and leaders to understand better and navigate the complexities of the workplace. By applying these theories, organisations can improve employee engagement and productivity and ultimately achieve their goals while adapting to an ever-changing business environment.