Overview of the Technology Acceptance Model (TAM)
Introduction to TAM
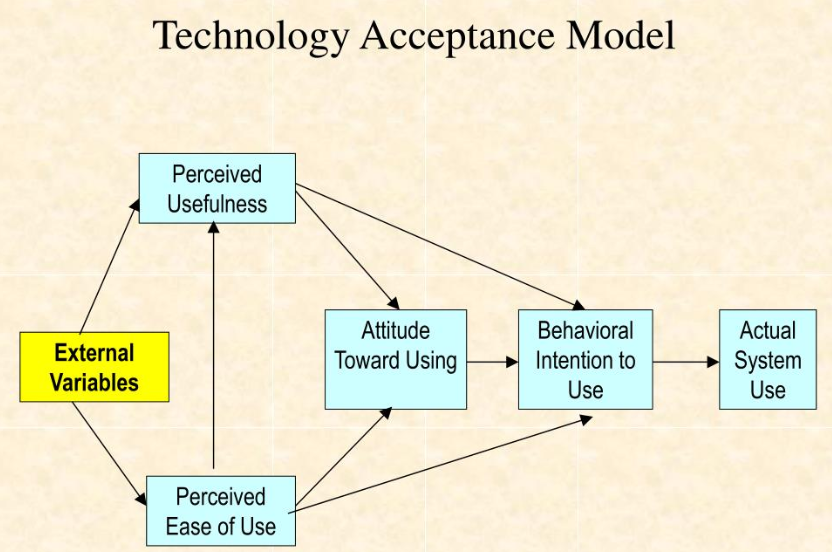
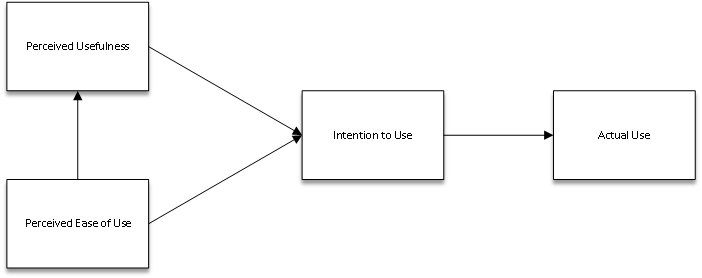
The Technology Acceptance Model (TAM) is a pivotal framework that seeks to explain how users come to accept and utilize new technologies. At its core, TAM postulates that perceived usefulness and perceived ease of use significantly influence user decisions regarding technology adoption. Familiarizing oneself with TAM can illuminate the path to understanding user behavior in various technological contexts, from simple mobile applications to complex information systems. This model serves as a guiding principle for researchers and developers alike. Organizations can tailor their innovations to meet user expectations more effectively by recognising the factors that drive user acceptance.
History and Development of TAM
TAM was first developed by Fred Davis in 1986 as part of his doctoral dissertation at MIT. It emerged from the larger field of social psychology and information systems. The model has since evolved through various iterations, reflecting the changing technology landscape and user interaction. Critical milestones in its history include:
- 1989: Introduction of the model in a seminal paper, sparking extensive research.
- 1996: Release of TAM 2, expanding the framework to include additional factors affecting adoption.
- 2003: Development of the Unified Theory of Acceptance and Use of Technology (UTAUT), further broadening the application of TAM principles.
These milestones underscore TAM’s robustness and adaptability, establishing it as a fundamental tool for understanding technology acceptance in diverse settings.

Understanding User Adoption
Factors Influencing User Adoption
Understanding user adoption requires a keen eye on the various elements influencing a user’s decision to embrace a new technology. Several factors come into play, including:
- Perceived Usefulness: Users are likely to adopt technology if they believe it enhances their productivity or lifestyle.
- Perceived Ease of Use: If technology is user-friendly and intuitive, the chances of adoption increase substantially.
- Social Influence: Recommendations from peers or the community can significantly impact a user’s decision.
Personal experience often reflects this; for instance, when exploring a new app, an endorsement from a friend can sway opinion more than marketing materials.
Behavioral Intention in User Adoption
Behavioral intention is the predictor of actual usage behavior in technology adoption. It represents the user’s motivation to engage with a technology. This intention can be cultivated by:
- Positive Experiences: Users with a successful initial interaction are likelier to continue using a technology.
- Continued Support: Access to support and resources can bolster a user’s confidence in adopting new technology.
By comprehensively analyzing these factors and intentions, organizations can better anticipate user behavior and design solutions that cater to their needs.
Components of the Technology Acceptance Model
Perceived Usefulness
The first essential component of the Technology Acceptance Model (TAM) is perceived usefulness. This refers to the degree to which a user believes a specific technology will enhance their performance or daily tasks. For example, consider how a project management tool like Asana can streamline team collaboration—its effectiveness directly influences its adoption. Users are more inclined to embrace technology that they believe will lead to tangible improvements in their productivity.
Perceived Ease of Use
Equally important is perceived ease of use, which describes how simple a technology is perceived. Users who find a tool complicated or cumbersome are likely to disengage. A personal anecdote could be using overly complex software for scheduling. My struggles with its navigation led me to seek alternatives with more intuitive interfaces, demonstrating how crucial ease of use is for encouraging adoption.
Attitude Toward Using
Next comes attitude toward using. This component encapsulates the user’s positive or negative feelings toward technology. Users may appreciate an app’s features but feel frustrated with its interface. This emotional response can greatly influence whether they engage with or abandon the technology.
Behavioral Intention
Lastly, we have behavioral intention, which indicates the likelihood of a user adopting and continuously using the technology. If a user develops a favorable attitude and recognizes the usefulness and ease of a system, they are more likely to intend to use it actively. Organizations must recognise these interrelated aspects to foster a user-centred approach that encourages successful adoption.
Applications of Technology Acceptance Model
Real-world Examples of TAM Implementation
The Technology Acceptance Model (TAM) has found its place in numerous industries, providing valuable insights into user adoption across diverse technologies. One prominent example is healthcare, where TAM has been utilized to evaluate electronic health record (EHR) systems. Studies revealed that perceived usefulness and ease of use significantly impacted healthcare professionals’ intention to adopt these systems. Another striking application is in e-learning platforms like Coursera, where TAM helps identify factors that drive students’ acceptance of online learning. Positive outcomes have been reported when institutions focus on enhancing ease of use and usefulness, thus creating a more engaging learning environment.
Benefits of Applying TAM in User Adoption Studies
The benefits of implementing TAM in user adoption studies are manifold:
- Targeted Improvements: Organizations can identify specific aspects of technology that require enhancement to boost user acceptance.
- Informed Decision-Making: Insights from TAM studies enable businesses to make data-driven decisions about technology investments.
- User Satisfaction: Companies can create solutions that genuinely resonate with their audience by understanding user perceptions.
Utilizing TAM streamlines the adoption process and contributes to a more satisfying experience for the end-user.
Criticisms and Limitations of the Technology Acceptance Model
Common Criticisms of TAM
Despite its widespread adoption and usefulness, the Technology Acceptance Model (TAM) has faced its share of criticisms. One significant point of contention is its oversimplification of user behavior. Critics argue that TAM does not fully account for the complexity of human motivations and the social context in which technology is adopted. For example, personal values and cultural influences often play substantial roles in user decisions, which TAM does not adequately encompass. Additionally, some researchers argue that TAM lacks predictive power. While it identifies correlations between perceptions and usage behavior, it may not fully capture all variables affecting user adoption in every context, leading to potential gaps in understanding.
Challenges in Applying TAM
Applying TAM can also present challenges.
- Context Dependency: The model may not translate well across different industries or user groups, as perceptions vary widely.
- Dynamic Technology Landscape: Rapid technological advancements can render established frameworks like TAM less relevant over time.
In my experience, while TAM provides solid foundational insights, addressing its limitations is crucial for achieving a more holistic understanding of user adoption in a continually evolving technological landscape.
Enhancements and Extensions of the Technology Acceptance Model
TAM 2
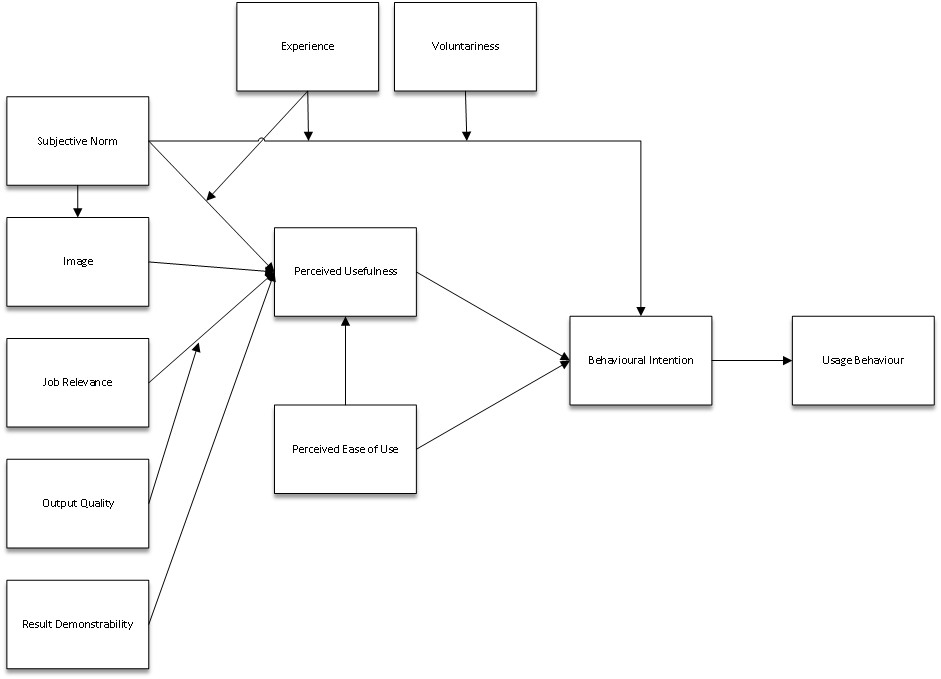
In response to the limitations identified in the original Technology Acceptance Model (TAM), TAM 2 was introduced in 2000 by Venkatesh and Davis. This enhanced version includes additional factors influencing user acceptance, notably social influence and cognitive instrumental processes. For example, social factors such as peer pressure can significantly affect an individual’s intention to adopt a new technology, as I witnessed during a workplace transition to a new project management tool. Many of my colleagues were influenced by those already using it. Integrating these broader influences enhances the model’s applicability, allowing it to capture various motivational factors.
Unified Theory of Acceptance and Use of Technology (UTAUT)
Building upon TAM and its predecessors, the Unified Theory of Acceptance and Use of Technology (UTAUT) consolidates eight models into one comprehensive framework. Introduced by Venkatesh et al. in 2003, UTAUT includes four key constructs: performance expectancy, effort expectancy, social influence, and facilitating conditions. This holistic approach allows organizations to comprehensively address user adoption, factoring in individual perceptions and external influences like resources and support. For instance, understanding the facilitating conditions can be pivotal for successful adoption when implementing a new enterprise software. By leveraging these enhanced models, organizations are better equipped to foster user acceptance and maximize the effectiveness of their technology initiatives.
Case Studies Using Technology Acceptance Model
Healthcare Industry Case Study
The Technology Acceptance Model (TAM) has been instrumental in analyzing the adoption of electronic health record (EHR) systems in the healthcare sector. A study conducted in a large hospital revealed that perceived usefulness was a significant predictor of physicians’ acceptance of EHRs. Many doctors noted that the system improved patient care and streamlined workflows. However, perceived ease of use also played a critical role. When the hospital provided comprehensive training and ongoing support, user acceptance surged. For instance, after implementing a mentorship program where tech-savvy staff helped their colleagues, adoption rates increased by nearly 30%. This case demonstrates the importance of addressing both aspects of TAM to ensure successful technology implementation in healthcare.
E-commerce Platform Case Study
Turning to e-commerce, a study on an online retail platform highlighted the relevance of TAM in understanding customer adoption. Consumers expressed heightened purchase intentions when they perceived the website as user-friendly and trustable. The research also found that strategies such as user reviews and recommendations greatly influenced perceived usefulness and ease of use. My experiences shopping on platforms that provide clear reviews resonate here; knowing others had positive experiences makes me more likely to buy. Consequently, applying TAM allowed the e-commerce company to refine its interface and boost user confidence, ultimately increasing sales and customer loyalty. Both cases exemplify the practical applications of TAM across various industries, providing invaluable insights into user behavior.
Future Trends and Implications
Emerging Technologies and TAM
As we look to the future, emerging technologies continue to reshape the landscape of user acceptance, creating new opportunities and challenges for the Technology Acceptance Model (TAM). For example, the rise of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning applications means users must now evaluate the potential usefulness and ease of use of increasingly complex systems. In my experience, applications like personalized recommendation engines have made shopping easier and altered how I perceive the usefulness of e-commerce platforms. As these technologies evolve, TAM must adapt to incorporate new factors, such as trust in AI decisions or data privacy concerns.
Importance of User-Centric Design
In this changing environment, the importance of user-centric design cannot be overstated. Technology that places user needs at the forefront—in terms of functionality, accessibility, and overall experience—will naturally align with the principles of TAM.
- Feedback Loops: Incorporating user feedback into the design process can lead to enhancements that resonate with user experiences.
- Iterative Development: Regular updates based on usage patterns can significantly improve perceived ease of use.
By emphasizing user-centric design principles, organizations can drive technology acceptance and foster long-term loyalty among users, creating a win-win scenario in an increasingly competitive market.

Conclusion and Key Takeaways
Summary of Technology Acceptance Model
In summarizing the Technology Acceptance Model (TAM), it’s essential to recognize its foundational role in understanding user behavior. TAM postulates that perceived usefulness and ease of use significantly influence an individual’s intention to accept and utilize new technology. It has proven adaptable to the dynamic technological landscape through its evolution, including enhancements like TAM 2 and the UTAUT framework. Reflecting on personal experiences, I’ve seen firsthand how these factors impact day-to-day decisions—from choosing software for work to selecting apps for personal use. When a tool is user-friendly and beneficial, it’s much more likely to be adopted.
Implications for Understanding User Adoption
The implications for understanding user adoption are profound. Organizations prioritising these insights can design technologies that meet user needs and foster long-term engagement.
- User-Centric Approach: Focusing on user perceptions can increase satisfaction and adoption rates.
- Continuous Feedback: Actively seeking user feedback can guide enhancements and innovations.
Ultimately, by applying the principles of TAM, businesses can better navigate the complex journey of technology adoption, ensuring that they remain responsive to user needs and preferences in an ever-evolving landscape.