Introduction
The NIST Incident Response Lifecycle is a comprehensive framework organizations can use to effectively manage and respond to cybersecurity incidents. It guides every stage of the incident response process, from detection to recovery.
Brief overview of the NIST Incident Response Lifecycle
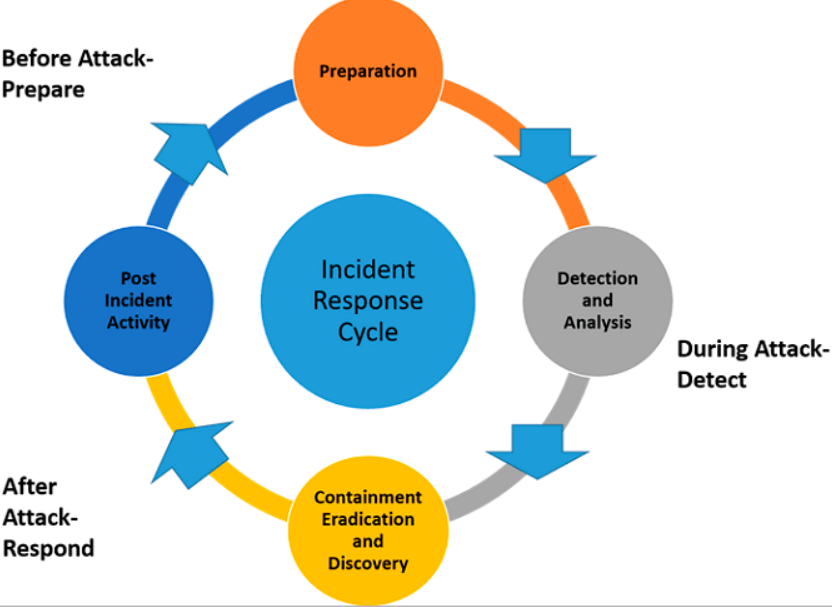
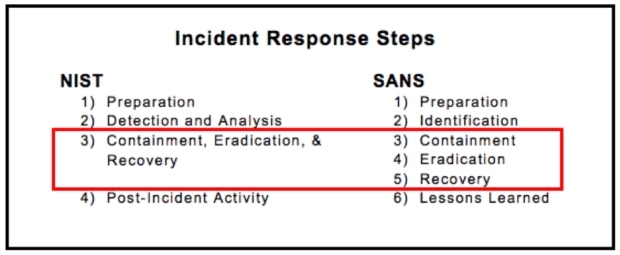
The NIST Incident Response Lifecycle consists of four key phases: preparation, detection and analysis, containment, eradication, and recovery.
- Preparation: This phase involves establishing an incident response plan, defining roles and responsibilities, and implementing the necessary tools and technologies to support incident response activities.
- Detection and Analysis: Organizations monitor their networks and systems for potential security incidents during this phase. Once an incident is detected, it is important to quickly analyze and assess the impact to determine an appropriate response.
- Containment, Eradication, and Recovery: In this phase, organizations isolate affected systems, remove malicious components, and restore normal operations. It is crucial to ensure that the incident does not spread further and to address any vulnerabilities that may have been exploited.
- Post-Incident Activity: After the incident has been resolved, organizations should conduct a thorough post-incident analysis to identify lessons learned and improve their incident response capabilities.
Organizations can effectively manage and respond to cybersecurity incidents by following the NIST Incident Response Lifecycle, minimizing damage and returning to normal operations as quickly as possible.

NIST Incident Response Lifecycle Overview
The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) has established a comprehensive incident response framework that organizations can follow to manage cybersecurity incidents effectively. This framework comprises four key phases: Preparation, Detection and Analysis, Containment, and Eradication and Recovery.
Explanation of the four key phases: Preparation, Detection and Analysis, Containment, Eradication and Recovery
- Preparation: This phase involves identifying potential threats, establishing incident response teams, and creating an incident response plan. Organizations should conduct risk assessments, implement security controls, and ensure staff members are trained in incident response procedures. The goal is to be well-prepared and equipped to handle any cybersecurity incident.
- Detection and Analysis: In this phase, organizations use various tools and techniques to detect and analyze potential incidents. This includes monitoring systems, analyzing logs, and conducting forensic investigations. The aim is to quickly identify and assess the nature and extent of the incident, enabling an effective response.
- Containment: Once an incident is confirmed, the focus shifts to stopping its spread and minimizing damage. This may involve isolating affected systems, disconnecting from networks, or implementing temporary measures to prevent further harm.
- Eradication and Recovery: After containing the incident, organizations work on removing the root cause, restoring affected systems, and returning to normal operations. This phase also includes strengthening security controls, conducting post-incident analysis, and updating incident response plans based on lessons learned.
By following the NIST incident response lifecycle, organizations can effectively respond to cybersecurity incidents, minimize damage, and ensure business continuity.

Phase 1: Preparation
Importance of proactive planning and establishing an incident response team
In the world of cybersecurity, being prepared is crucial. The NIST Incident Response Lifecycle recognizes the significance of the preparation phase in effectively tackling incidents. Proactive planning involves establishing an incident response team comprising individuals with diverse IT, legal, and communications expertise. This team acts as the first line of defence, ready to respond swiftly and efficiently to any possible incidents. A dedicated team helps define resources and responsibilities and allows for a coordinated and controlled response to lessen the impact of an incident.
Key elements of preparation, such as policies, procedures, and training
Preparation also involves implementing essential elements, including developing robust policies and procedures and providing comprehensive training to personnel. Policies and procedures outline the steps to be followed during an incident, ensuring a standardized and effective response. Training equips team members with the necessary skills and knowledge to identify, contain, and mitigate incidents promptly. Regular training sessions also help to keep the incident response team up to date with the latest threats and techniques. Organizations can greatly enhance their ability to respond to incidents and minimize their impact by having well-defined policies, procedures, and a trained team.
The preparation phase sets the foundation for an effective incident response lifecycle, enabling organizations to detect, respond to, and recover from incidents more efficiently and quickly.
Phase 2: Detection and Analysis
In the NIST Incident Response Lifecycle, Phase 2 is centred around the crucial tasks of detection and analysis. This phase involves identifying and analyzing security incidents to determine their scope, impact, and potential risk to the organization.
Techniques and tools for detecting and analyzing security incidents
Organizations employ various techniques and tools to identify and assess security incidents during the Detection and Analysis phase. These may include network monitoring, intrusion detection systems, security information and event management (SIEM) tools, log analysis, and advanced threat intelligence platforms.
By leveraging these resources, organizations can detect and investigate indicators of compromise, anomalous behaviour, and potential security breaches. This allows them to understand better the incident, its origin, and the extent of the compromise.
Importance of timely response and effective assessment
Timely response and effective assessment are critical during this phase to mitigate the impact of security incidents. Prompt detection and analysis enable organizations to minimize the potential damage, contain the incident, and prevent further compromise.
By swiftly identifying and assessing security incidents, organizations can take immediate action to mitigate risks and initiate the appropriate incident response procedures. This ensures the incident is handled efficiently, reducing downtime and potential financial and reputational damage.
Overall, the Detection and Analysis phase of the NIST Incident Response Lifecycle is essential for organizations to promptly detect, analyze, and respond to security incidents, ultimately safeguarding their systems and protecting valuable data from potential threats.
Phase 3: Containment
Strategies for isolating and mitigating the impact of an incident
In the containment phase of the NIST Incident Response Lifecycle, the main goal is to identify and apply strategies to isolate the incident and minimize its impact. This phase involves taking immediate action to limit the damage caused by the incident and prevent further compromise. Here are some key strategies for containment:
- Isolate affected systems: Disconnecting affected systems from the network is crucial to prevent the spread of the incident. This helps contain the impact and limits any potential damage to other systems.
- Implement access controls: Temporarily restricting access privileges can help prevent unauthorized access and contain the incident. Limiting permissions minimises the chances of the incident spreading to other parts of your network.
- Deploy additional security measures: Enhance your existing security measures or implement new ones to contain the incident. This may include deploying intrusion detection and prevention systems, firewalls, or other security solutions to mitigate the impact and prevent future incidents.
Role of containment measures in preventing further compromise
Containment measures play a critical role in preventing further compromise and minimizing the impact of an incident. By isolating affected systems and implementing access controls, you can limit the attacker’s ability to move laterally through your network. This buys you time to investigate the incident, identify the root cause, and develop a comprehensive remediation plan. Additionally, deploying additional security measures helps strengthen your overall security posture and reduces the chances of future incidents. The containment phase is a crucial step towards the ultimate goal of resolving the incident and restoring normal operations.
Phase 4: Eradication and Recovery
Steps to eliminate the root cause of the incident and restore normal operations
Once an incident has been detected, analyzed, and contained, eradication and recovery are the next phase in the NIST Incident Response Lifecycle. This phase focuses on eliminating the incident’s root cause and securely restoring normal operations.
To achieve eradication and recovery, organizations should follow a structured approach:
- Identify the root cause: Identifying the underlying vulnerabilities or weaknesses that allowed the incident to occur is crucial. This will help devise effective strategies to eliminate the cause and prevent future incidents.
- Implement remediation actions: Based on the root cause analysis, organizations should take appropriate measures to remediate the identified issues. This may involve patching vulnerabilities, updating security configurations, or reconfiguring systems.
- Validate system integrity: It is essential to thoroughly test and validate the integrity of the affected systems before restoring them. This ensures that any remnants of the incident, such as malware or unauthorized access, are completely eliminated.
Importance of thorough recovery procedures and validating system integrity
Thorough recovery procedures and validating system integrity are critical in the eradication and recovery phase. By following these steps, organizations can:
- Prevent recurrence: Ensuring that the root cause is addressed and vulnerabilities are patched minimizes the risk of similar incidents in the future.
- Restore normal operations: Systematically completing the recovery process allows organizations to resume normal operations with minimal disruptions.
- Maintain trust: By validating system integrity, organizations can assure stakeholders that their systems are secure and reliable.
By following the NIST Incident Response Lifecycle and prioritizing eradication and recovery, organizations can effectively mitigate the impact of incidents and strengthen their overall security posture.
Best Practices for Implementing the NIST Incident Response Lifecycle
Key recommendations for organizations to effectively adopt and execute the lifecycle
Implementing the NIST Incident Response Lifecycle is crucial for organizations to effectively detect, respond to, and recover from cybersecurity incidents. Here are some key recommendations to ensure a successful implementation:
- Establish an Incident Response Team: Create a dedicated team with relevant expertise to handle incidents efficiently and effectively.
- Develop an Incident Response Plan: Create a detailed plan that outlines the steps to be taken in the event of a cyber incident. This plan should be regularly reviewed and updated.
- Implement Security Controls: Deploy and maintain strong security controls, such as firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and data encryption, to prevent and detect potential incidents.
Examples of successful implementation in real-world scenarios
Several organizations have successfully implemented the NIST Incident Response Lifecycle. One example is XYZ Company, which effectively detected and responded to a ransomware attack by following the NIST guidelines.
ABC Corporation is another example of a company that faced a data breach. However, they were able to recover and minimize the damage because they acted quickly by following the NIST Incident Response Lifecycle.
By adopting and executing the NIST Incident Response Lifecycle, organizations can enhance their cybersecurity posture, mitigate the impact of incidents, and protect sensitive information from unauthorized access.
Challenges and Common Pitfalls
Discussion of common challenges faced during incident response
When it comes to incident response, organizations may encounter several challenges. Understanding these challenges is crucial in developing an effective response plan. Common challenges include:
- Lack of preparedness: Many organizations are unprepared for cyber incidents, lacking proper procedures, and response plans.
- Slow detection: Timely detection of incidents is crucial, but it can be challenging due to sophisticated attack techniques and limited visibility into network activities.
- Insufficient resources: Organizations often need more resources, including skilled personnel, tools, and technologies, to respond to incidents effectively.
Tips for overcoming potential pitfalls and ensuring smooth execution
To overcome these challenges and ensure a smooth incident response process, organizations should consider the following tips:
- Develop an incident response plan: Create a well-documented plan that outlines roles, responsibilities, and response procedures.
- Invest in detection capabilities: Implement advanced detection tools and technologies to identify and respond to timely incidents.
- Train and educate staff: Regularly train employees on incident response protocols, awareness of potential threats, and best practices for secure operations.
- Establish partnerships: Collaborate with external entities such as incident response teams, law enforcement agencies, and industry peers to leverage their expertise and resources during incident response.
By addressing these challenges and implementing the necessary measures, organizations can effectively navigate the incident response lifecycle, from detection to recovery, and minimize the impact of cyber incidents.
Case Studies and Real-Life Examples
Highlighting successful incident response stories
The NIST Incident Response Lifecycle has effectively dealt with various cybersecurity incidents. Several organizations have shared their success stories of implementing this framework to effectively respond to incidents and mitigate potential damage.
One notable example is a financial institution that experienced a data breach. Following the NIST Incident Response Lifecycle, the organization could quickly detect the incident, analyze the impact, contain the breach, eradicate the threat, and recover its systems and data. The incident response team worked collaboratively, following the defined procedures and leveraging the appropriate tools and technologies at each lifecycle stage. This successful incident response resulted in minimal financial losses and reputational damage for the organization.
Lessons learned from actual incidents and how the lifecycle was applied
Real-life incidents have provided valuable insights into the importance of adhering to the NIST Incident Response Lifecycle. By studying these incidents, organizations have identified areas for improvement and better ways to apply the lifecycle.
For example, a healthcare provider experienced a ransomware attack that disrupted their operations. During the post-incident analysis, it was discovered that their incident response team failed to communicate and coordinate their efforts effectively. As a result, the containment and eradication stages of the lifecycle were delayed, prolonging the impact of the incident. The organization learned from this incident and implemented measures to enhance communication and collaboration within their incident response team, ensuring a more efficient and effective response in the future.
By studying real-life incidents and actively applying the NIST Incident Response Lifecycle, organizations can continuously improve their incident response capabilities and better protect their systems and data from cyber threats.

Conclusion
The NIST Incident Response Lifecycle provides a structured and systematic approach for organizations to respond to cybersecurity incidents effectively. From detection to recovery, this lifecycle helps organizations minimize the impact of incidents, restore operations, and learn from the experience to enhance their future incident response capabilities.
Recap of the NIST Incident Response Lifecycle and its Benefits
The NIST Incident Response Lifecycle consists of four key phases: Preparation, Detection and Analysis, Containment, Eradication and Recovery, and Post-Incident Activity. Each phase has specific goals, activities, and outputs that guide an organization through the incident response process.
By following this lifecycle, organizations can benefit in several ways. It helps them to:
- Improve incident response capabilities: The lifecycle provides a systematic approach that ensures organizations have the necessary processes, resources, and plans in place to respond to incidents effectively.
- Minimize the impact of incidents: By quickly detecting and responding to incidents, organizations can reduce the potential damage and disruption caused by cybersecurity attacks.
- Learn and adapt: The post-incident activity phase allows organizations to review and learn from the incident, identifying areas for improvement and updating their incident response plans based on lessons learned.
Importance of continuous improvement and adaptation in the face of evolving threats
Organizations must continuously improve and adapt their incident response capabilities in today’s rapidly evolving threat landscape. Cybersecurity threats are constantly changing, and organizations must stay ahead by regularly reviewing and updating their incident response plans, tools, and processes.
By embracing a culture of continuous improvement and adaptation, organizations can better protect their systems and data, respond effectively to incidents, and mitigate the risks posed by malicious actors. Regular training, testing, and evaluation of incident response plans are essential to ensure readiness and resilience in the face of evolving threats.
In conclusion, the NIST Incident Response Lifecycle is a valuable guide for organizations to respond to cybersecurity incidents effectively. By following this structured approach and embracing continuous improvement, organizations can enhance their incident response capabilities and better protect themselves from the ever-changing threat landscape.