Introduction
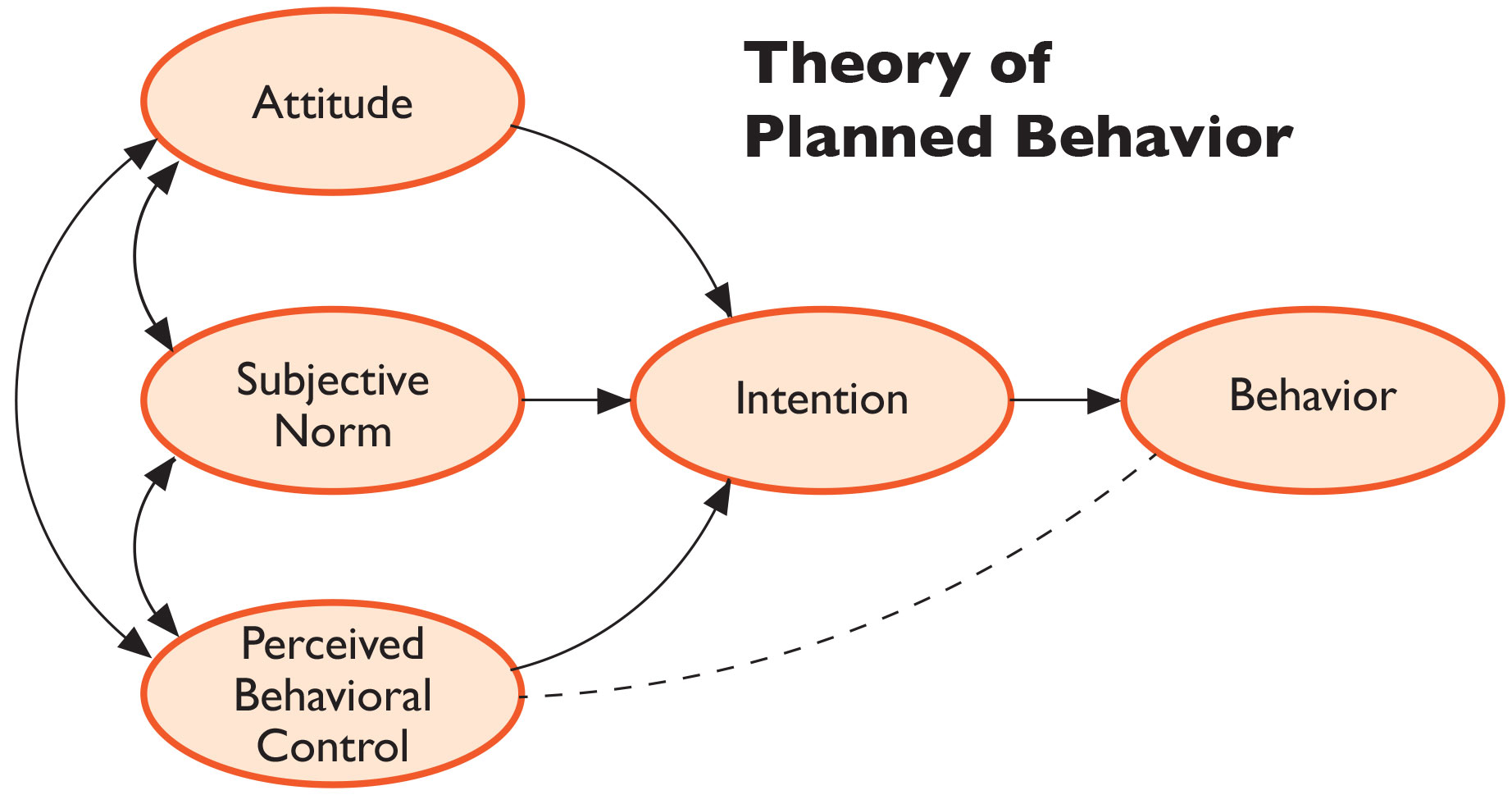
The Theory of Planned Behaviour (TPB) is a widely recognized psychological theory that provides insights into human behavior and decision-making processes. In the context of technology adoption, understanding TPB can be crucial to successfully implementing new technologies in various industries.
Overview of the Theory of Planned Behaviour
The TPB suggests that an individual’s intention to perform a specific behavior is influenced by three main factors: attitude, subjective norms, and perceived behavioral control.
- Attitude: Attitude refers to an individual’s perceptions and evaluations of the behavior in question. In the case of technology adoption, a positive attitude towards the new technology can significantly increase the likelihood of adoption.
- Subjective Norms: Subjective norms reflect the influence of social factors on an individual’s behavior. People are more likely to adopt a technology if they perceive that their peers or important others expect them to do so.
- Perceived Behavioral Control: Perceived behavioral control relates to an individual’s perception of their ability to perform the behavior successfully. Self-efficacy and access to necessary resources can influence perceived behavioral control.
Importance of Technology Adoption in Today’s World
Technology adoption drives innovation, productivity, and competitiveness in today’s rapidly evolving business landscape. Organizations that embrace new technologies are better positioned to streamline processes, enhance customer experiences, and gain a competitive advantage.
Understanding the Theory of Planned Behaviour can help businesses effectively navigate the challenges associated with technology adoption. By addressing attitudes, subjective norms, and perceived behavioral control, organizations can increase the likelihood of successful technology adoption and realize its benefits.

Components of the Theory of Planned Behaviour
The Theory of Planned Behaviour (TPB) is a psychological framework that explains human behavior, particularly in the context of technology adoption. It suggests that an individual’s intentions to adopt technology are influenced by three core components: attitude towards technology, subjective norms, and perceived behavioural control.
Attitude towards Technology
Attitude towards technology refers to an individual’s positive or negative evaluation of using a particular technology. It involves perceptions of usefulness, ease of use, and overall satisfaction with the technology. Positive attitudes are more likely to result in higher intentions to adopt the technology.
Subjective Norms
Subjective norms are social influences that shape an individual’s intentions to adopt a technology. They are based on the beliefs and expectations of significant others such as friends, family, and colleagues. If an individual perceives that important people in their life encourage or support using a specific technology, it increases their intention to adopt it.
Perceived Behavioral Control
Perceived behavioral control refers to an individual’s belief in their ability to adopt and use a technology successfully. It incorporates factors such as self-efficacy, perceived barriers, and facilitators. Higher levels of perceived behavioral control lead to more excellent intentions to adopt the technology.
Understanding these components can help organizations design effective strategies to promote technology adoption. By addressing attitudes towards technology, subjective norms, and perceived behavioral control, businesses can increase the likelihood of successfully adopting and implementing their technology solutions.

Attitude towards Technology
Technology adoption plays a critical role in the success of businesses and individuals. Understanding the factors influencing attitudes towards technology can provide valuable insights for successful adoption.
Factors influencing Attitude towards Technology
- Perceived usefulness: Users are likelier to adopt a new technology if they believe it will enhance their performance, productivity, or personal convenience.
- Perceived ease of use: Potential users are more likely to adopt a technology perceived as easy to use. User-friendly interfaces and clear instructions can significantly influence attitudes.
- Social norms: The influence of friends, colleagues, or industry experts can shape an individual’s perception of age adoption, while harmful norms can create hesitation.
Methods to Influence Attitude towards Technology
- Educational programs: Providing comprehensive training and educational resources on the benefits and usage of the technology can help overcome resistance and instil a positive attitude towards adoption.
- Testimonials and case studies: Sharing success stories and real-life examples of how the technology has improved business operations or personal lives can create a positive perception and increase adoption rates.
- Accessibility: Ensuring easy access to the technology through user-friendly platforms and intuitive interfaces can foster a positive attitude among potential users.
By understanding the theory of planned behavior and its influence on technology adoption, businesses and individuals can make informed decisions and successfully incorporate new technologies into their operations and daily lives.
Subjective Norms
When it comes to successful technology adoption, subjective norms play a significant role. These norms refer to the influence of social factors on an individual’s decision to adopt a new technology. Understanding and leveraging subjective norms can significantly enhance the chances of successful technology adoption.
Influence of Social Factors on Technology Adoption
Social factors have a powerful impact on our beliefs, attitudes, and behaviors. When adopting new technology, people tend to look to others for cues on what is acceptable and appropriate. This is where subjective norms come into play.
For example, if influential individuals or groups in a person’s social network already use a particular technology and endorse its benefits, it creates a positive perception of the technology. This positive perception can significantly influence an individual’s intention to adopt the technology.
Methods to Influence Subjective Norms
- Social Proof: Highlighting testimonials, case studies, or success stories from individuals or businesses that have successfully adopted the technology can create a sense of social proof. This can help shape subjective norms by showcasing positive experiences and outcomes.
- Influencer Marketing: Collaborating with influencers or industry experts with a strong following can provide credibility and influence subjective norms. Their endorsement of the technology can make it more appealing and acceptable to potential adopters.
- User Communities: Building user communities around the technology fosters user interaction and cultivates a sense of belonging. This can create a positive normative influence as users share their experiences and provide support to each other.
By understanding the power of subjective norms and implementing strategies to shape them positively, businesses can increase the chances of successful technology adoption among their target audience.
The Theory of Planned Behaviour: A Guide to Successful Technology Adoption
The Theory of Planned Behaviour (TPB) is a widely recognized framework that explains human behavior. When it comes to technology adoption, understanding this theory can help businesses develop strategies to increase the likelihood of successful adoption.
Perceived Behavioural Control
Definition: Perceived Behavioural Control refers to an individual’s belief in their ability to perform a behavior and achieve the desired outcome. In the context of technology adoption, it represents the user’s perception of their ability to use it effectively.
Factors Affecting Perceived Behavioural Control
- Self-efficacy: The individual’s confidence in their technology use plays a crucial role in perceived behavioural control.
- Training and Support: Access to training resources and technical support can significantly enhance an individual’s sense of control over the technology.
- Past Experience: Previous positive experiences with similar technologies can increase perceived behavioural control.
Methods to Enhance Perceived Behavioural Control
- User-friendly Interfaces: Designing intuitive and easy-to-use interfaces can boost users’ perceived behavioural control.
- Provide Clear Instructions: Clear and concise instructions that guide users through the adoption process can increase their confidence and sense of control.
- Ongoing Support: Offering ongoing technical support and assistance can help users overcome challenges and reinforce their belief in their ability to use the technology.
By considering these factors and implementing strategies to enhance perceived behavioural control, businesses can increase the likelihood of successful technology adoption and improve user satisfaction.

Successful Technology Adoption Strategies
When successfully implementing new technology in your business, understanding the theory of planned behavior can be a game-changer. This theory suggests that people are more likely to adopt new technology if they perceive it as valid, believe that they have control over using it, and consider it to align with their values and beliefs. Here are a few strategies to help you leverage this theory and drive successful technology adoption.
Understanding User Needs and Preferences
One crucial factor in technology adoption is understanding your users’ needs and preferences. Conduct research and gather feedback from your target audience to identify pain points and areas where technology can provide solutions. You increase the likelihood of adoption by aligning your technology with their specific needs.
Providing Training and Support
Offering comprehensive training and ongoing support is vital for successful technology adoption. Many users may resist change due to fear of being unable to use the technology effectively. By providing training materials, tutorials, and accessible customer support channels, you can empower users to overcome their apprehensions and embrace the new technology.
Creating a Positive User Experience
The user experience plays a crucial role in technology adoption. Ensure your technology is designed intuitively, with a user-friendly interface that minimizes complexity. Focus on enhancing usability, efficiency, and satisfaction to create a positive user experience that encourages adoption.
By implementing these strategies based on the theory of planned behavior, you can increase the chances of successful technology adoption in your business. Remember to continuously gather feedback, monitor usage patterns, and adjust as needed to ensure maximum acceptance and utilization of the new technology.
Case Studies
Successfully adopting new technology and understanding the Theory of Planned Behavior is crucial. By following this psychological framework, companies can increase the likelihood of successful implementation and adoption. This theory suggests that behavioral intention is influenced by three key factors: attitude towards the behavior, subjective norms, and perceived behavioral control.
Examples of Successful Technology Adoption
- Company A: Company A implemented a new project management software after conducting extensive research and identifying the benefits it would bring to their workflow. They also ensured that all employees received proper training and ongoing support. Company A successfully adopted the technology by emphasizing the software’s positive impact on their work processes and involving employees in the decision-making process.
- Company B: After facing challenges managing their customer relationship management (CRM) system, Company B adopted a new CRM software. They involved key stakeholders from different departments and sought their input on the selection process. Company B successfully adopted the new CRM system by addressing concerns, accommodating feedback, and providing comprehensive training.
Lessons Learned from Successful Implementations
- Understand employee attitudes: Recognize that employees’ attitudes towards the new technology play a significant role in adoption. Address any concerns or resistance early on to build a positive attitude.
- Involve key stakeholders: Engage employees at different levels in decision-making to ensure buy-in and ownership of the new technology.
- Provide training and support: Comprehensive training programs and ongoing support are essential for successful adoption. This helps employees feel confident and capable in using the technology effectively.
By following these examples and lessons learned, businesses can increase the chances of successful technology adoption using the Theory of Planned Behavior as a guide.
Overcoming Barriers to Technology Adoption
The Theory of Planned Behaviour (TPB) is useful in understanding and addressing the barriers to successful technology adoption. Organizations can increase the likelihood of successful adoption by identifying and addressing resistance to change and dealing with technological anxiety.
Identifying and Addressing Resistance to Change
Resistance to change is a common barrier to technology adoption. To overcome this, it is essential to communicate the benefits of the new technology to employees at all levels. This highlights how the technology will improve efficiency, productivity, and job satisfaction. Additionally, involving employees in decision-making and providing training and support throughout the transition can help alleviate resistance.
Dealing with Technological Anxiety
Technological anxiety may arise from a fear of the unknown or a lack of confidence in using new technology. To address this, organizations should provide comprehensive training programs to ensure employees feel comfortable using the technology. Additionally, clear communication about the expected outcomes of adopting the technology can help alleviate anxiety and create a sense of purpose and excitement among employees.
By applying the principles of the Theory of Planned Behaviour, organizations can overcome barriers to technology adoption and increase the likelihood of successful implementation. Understanding and addressing resistance to change and technological anxiety are crucial in ensuring a smooth transition to new technologies.
Summary of the Theory of Planned Behaviour and its Application to Technology Adoption
The Theory of Planned Behaviour (TPB) is a widely recognized framework that seeks to explain human behavior, specifically in the context of technology adoption. According to the TPB, an individual’s intention to adopt a particular technology is influenced by three key factors: attitude towards the behavior, subjective norms, and perceived behavioral control.
Attitude towards the behavior refers to the individual’s positive or negative evaluation of adopting the technology. Subjective norms consider the social pressures or expectations influencing one’s decision to adopt technology. Lastly, perceived behavioral control refers to an individual’s perception of their ability to adopt and use the technology successfully.
Successful technology adoption requires a positive attitude, social support or encouragement from others, and a belief in one’s ability to overcome potential challenges.
Future Trends in Technology Adoption
As technology advances rapidly, new technologies are expected to be adopted. Key trends in technology adoption include:
- Integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML): AI and ML technologies are becoming increasingly prevalent in various industries. Businesses that embrace these technologies are likely to gain a competitive edge.
- Internet of Things (IoT): The IoT refers to the interconnection of everyday objects via the internet. As IoT devices become more common, their adoption will increase across smart homes, healthcare, transportation, and other sectors.
- Virtual and Augmented Reality (VR/AR): VR and AR technologies are transforming industries such as gaming, entertainment, education, and healthcare. Their adoption is expected to grow as these immersive experiences become more accessible.
In conclusion, understanding the Theory of Planned Behaviour can help businesses effectively strategize their technology adoption efforts. Embracing future trends in technology can lead to increased efficiency, improved customer experiences, and a competitive advantage in the digital age.