Introduction to Unconscious Biases
Unconscious bias refers to the attitudes or stereotypes that affect our decision-making processes without us even realizing it. These biases can significantly impact the workplace, influencing hiring decisions, promotions, and overall workplace dynamics. To build a more inclusive and equitable workplace, it is crucial to understand and address unconscious bias.
Definition of Unconscious Bias
Unconscious bias, also known as implicit bias, are deeply ingrained stereotypes and prejudices that are unintentional and automatic. They are formed through societal conditioning and personal experiences, often leading to discriminatory behavior without conscious awareness.
Importance of Understanding and Addressing Unconscious Bias
Recognizing unconscious biases is essential for fostering workplace diversity, inclusion, and equality. Understanding how these biases can influence our perceptions and actions can create a more inclusive environment that values everyone’s contributions.
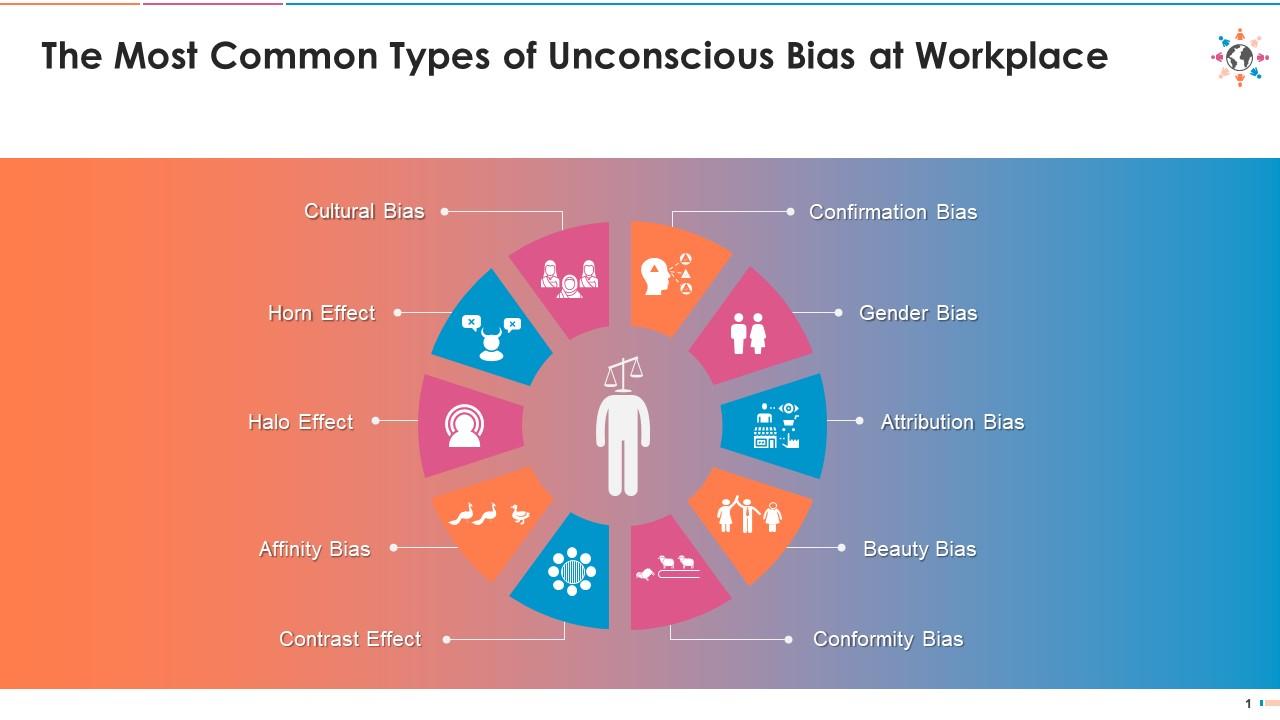
Types of Unconscious Bias:
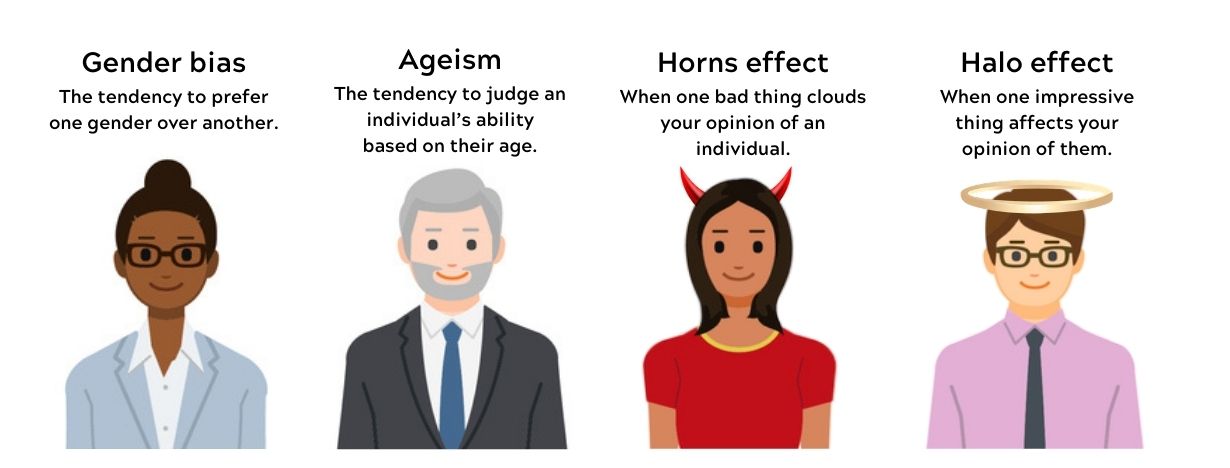
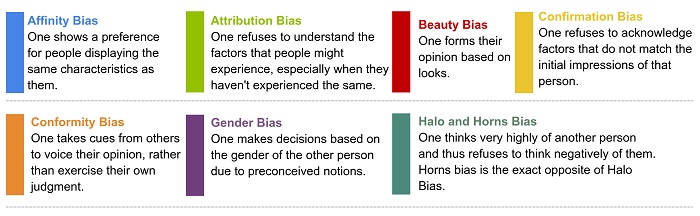
- Confirmation Bias: This occurs when individuals seek information confirming their beliefs while dismissing contradictory evidence.
- Halo Effect: The tendency to judge someone based on one positive trait or characteristic, overlooking their other qualities or shortcomings.
- Stereotyping: Generalizing characteristics or traits about a group of people based on assumptions or preconceived notions.
- Affinity Bias: Favoring individuals similar to oneself in terms of background, interests, or demographics.
Effects of Unconscious Bias:
Unconscious bias can decrease workplace diversity, hinder collaboration and innovation, create a hostile work environment, and limit opportunities for underrepresented groups.
Solutions:
Increasing awareness through education and training programs, implementing blind recruitment processes, promoting diverse leadership initiatives, providing mentorship and sponsorship opportunities for marginalized groups can help address unconscious bias in the workplace.
By actively working towards identifying and mitigating unconscious biases, organizations can foster a more inclusive culture that values diversity and promotes equal opportunities for all.

Types of Unconscious Bias
Unconscious bias is a pervasive and often subtle issue that can adversely affect decision-making and workplace relationships. Understanding the different types of unconscious bias is the first step towards addressing and mitigating its impact in the workplace.
Implicit bias
Implicit bias refers to the biases that individuals hold without their conscious awareness. These biases are often shaped by societal stereotypes and can influence our judgments and behaviors towards certain groups of people. Recognizing our implicit biases is key to minimizing their influence on our decision-making processes.
Confirmation bias
Confirmation bias occurs when individuals seek out or interpret information in a way that confirms their pre-existing beliefs or biases. This can lead to a distorted perception of reality and hinder objective decision-making. Overcoming confirmation bias requires actively seeking diverse perspectives and challenging our own assumptions.
Halo effect
The halo effect is a cognitive bias in which our overall impression of a person influences our judgments about their traits or abilities. For example, if someone is physically attractive, we might automatically assume they are also intelligent or talented. Awareness of this bias can help us make more accurate assessments based on objective criteria rather than superficial attributes.
It is important for organizations to create awareness about unconscious biases in the workplace and provide training programs to address and mitigate their impact. Encouraging diversity and inclusion, promoting empathy, and fostering open dialogue can all contribute to creating a more inclusive work environment where unconscious biases are recognized and challenged. By acknowledging and actively addressing unconscious bias in the workplace, organizations can foster fairness, equality, and innovation among their employees.
Confirmation Bias
Confirmation bias is a common unconscious bias that affects decision-making and team dynamics in the workplace. It occurs when individuals seek out information or interpret evidence in a way that confirms their pre-existing beliefs or assumptions. This bias can hinder an organization’s ability to make objective and informed decisions, leading to suboptimal outcomes and reduced team effectiveness.
Definition and examples of confirmation bias
Confirmation bias refers to the tendency to favor information that supports one’s existing beliefs while discounting or ignoring contradictory evidence. For example, a manager may disregard negative feedback about an employee because it goes against their perception of that employee’s performance. Another example is when team members gravitate towards ideas or data that align with their own opinions, disregarding alternative viewpoints.
Impact of confirmation bias on decision-making and team dynamics
Confirmation bias can negatively impact decision-making processes within a workplace. When individuals only consider information that confirms their biases, they may overlook valuable insights and perspectives that could lead to better decisions. This can result in missed opportunities, increased groupthink, and decreased team innovation.
Additionally, confirmation bias can create tension and hinder effective collaboration among team members. When people dismiss or downplay differing viewpoints, it can lead to conflicts, decreased trust, and a lack of psychological safety within the group.
Strategies to mitigate confirmation bias
To address confirmation bias in the workplace, organizations can implement various strategies. Promoting diversity and inclusion, encouraging open dialogue, active listening, seeking alternative perspectives, conducting thorough research and analysis, involving multiple stakeholders with diverse backgrounds in decision-making processes.
Training programs on unconscious biases can also raise awareness about confirmation bias and provide tools for individuals to recognize and challenge their own biases. Creating a culture that values critical thinking, evidence-based decision-making, and respectful debate can help mitigate the negative impact of confirmation bias on organizational outcomes.
Halo Effect in the Workplace
The workplace is not immune to unconscious bias. The halo effect is one common bias that can impact our perceptions and evaluations. Understanding this bias and its effects is crucial for creating inclusive work environments.
Definition and examples of the halo effect
The halo effect refers to the tendency to form an overall positive impression of someone based on one specific positive trait or characteristic. If a colleague looks attractive, we often think they are good at their job, even if we don’t have much evidence to back this up.
How the halo effect influences perceptions and evaluations
The halo effect can lead to biased judgments and decisions in the workplace. It can result in individuals being evaluated more positively or receiving preferential treatment based on unrelated qualities such as appearance, likability, or personal connections. This bias can impact hiring, performance evaluations, promotions, and other crucial decisions.
Steps to minimize the halo effect in the workplace
To mitigate the impact of the halo effect, organizations can take several steps:
- Raise awareness: Educate employees about unconscious bias and the halo effect specifically. Encourage them to critically evaluate their judgments and consider multiple factors.
- Implement structured processes: Use standardized criteria and objective measures when evaluating employees’ performance and potential. This reduces the influence of subjective impressions and focuses on concrete evidence.
- Provide training: Offer training programs that teach employees how to recognize, mitigate, and prevent biases. This can help create a more inclusive and fair work environment.
- Foster diversity and inclusion: Actively promote diversity in recruitment and ensure representation throughout all levels of the organization. Encouraging diverse perspectives helps challenge biases and combat the halo effect.
By addressing unconscious biases like the halo effect, organizations can create a workplace where all employees are evaluated and treated fairly, enhancing overall productivity and satisfaction.

Effects of Unconscious Bias in the Workplace
Unconscious bias in the workplace can significantly affect employee engagement, diversity and inclusion efforts, decision-making, and innovation. Understanding these effects is crucial for creating a fair and inclusive work environment.
Impact on employee engagement and satisfaction
Unconscious bias can create a hostile work environment for employees negatively affected by the biases. It can lead to feelings of exclusion, reduced motivation, and lower job satisfaction. This, in turn, can result in decreased productivity and increased turnover rates.
Barriers to diversity and inclusion
Unconscious bias can create barriers to achieving diversity and inclusion goals within organizations. Biases such as confirmation bias, halo effect, and stereotyping can lead to hiring and promotion decisions that favor certain groups over others, perpetuating inequality and limiting opportunities for underrepresented individuals.
Implications for decision-making and innovation
Unconscious bias can also impact decision-making processes within organizations. When biases shape decision-making, it can hinder creativity, limit diverse perspectives, and prevent innovative ideas from being considered. This can hinder organizational growth and competitive advantage.
To address unconscious bias in the workplace, organizations should implement training programs to raise awareness of biases and provide tools to mitigate their impact. Creating a culture of inclusivity and accountability is crucial. Additionally, organizations should establish fair hiring and promotion practices that emphasize meritocracy over personal biases.
By addressing unconscious bias head-on, organizations can create an environment that fosters employee engagement, enhances diversity and inclusion efforts, and promotes effective decision-making for long-term success.
Solutions to Address Unconscious Bias
In order to create a truly inclusive and diverse workplace, it is important for organizations to tackle unconscious bias head-on. Here are some effective solutions that can help address unconscious bias in the workplace.
Training programs and workshops
One of the most effective ways to address unconscious bias is through training programs and workshops. These initiatives can provide education on unconscious bias, its impact, and strategies to overcome it. By increasing awareness and understanding, employees can start to recognize their own biases and learn how to challenge them.
Creating a culture of inclusion and awareness
Organizations should strive to create a culture that encourages diversity and inclusion. This involves fostering an environment where individuals from different backgrounds feel valued and respected. By promoting inclusivity and celebrating diversity, organizations can help reduce the impact of unconscious bias.
Encouraging open dialogue and feedback
Open dialogue and feedback are essential for addressing unconscious bias. Organizations should encourage employees to speak up about instances of bias they may witness or experience. Regular feedback sessions can also help identify any unconscious biases that may be affecting decisions or actions within the organization.
By implementing these solutions, organizations can work towards minimizing the impact of unconscious bias in the workplace. Education, inclusive culture, and open dialogue can create an environment of value and respect for all, regardless of background.
Unconscious Bias in the Workplace: Understanding and Addressing
Unconscious bias refers to people’s automatic associations and attitudes towards certain individuals or groups, often without even realizing it. Recognizing and addressing these biases is critical in creating a more inclusive and equitable workplace environment.
Types of Unconscious Bias
- Confirmation Bias: The tendency to seek information confirming pre-existing beliefs, while disregarding contradictory evidence.
- Halo Effect: When a positive impression of a person or group influences judgments about their other characteristics, regardless of their actual abilities or performance.
- Stereotyping: Generalizations made about individuals based on their membership in a particular group, often leading to unfair assumptions and judgments.
- Affinity Bias: Favoring individuals who share similar backgrounds, experiences, or attributes, which can result in overlooking qualified candidates who bring diversity to the table.
Effects and Solutions
Unconscious bias can have detrimental effects on recruitment, promotion, and overall workplace dynamics. To address these biases:
- Educate: Provide training programs to raise awareness about unconscious bias and its impact on decision-making processes.
- Implement Blind Processes: Remove identifying information from resumes and applications to ensure unbiased evaluation of candidates.
- Promote Diversity and Inclusion: Actively seek diverse perspectives in decision-making roles, fostering an inclusive environment where different voices are heard and valued.
Conclusion
Recognizing and addressing unconscious bias is an ongoing effort that requires commitment and dedication from both individuals and organizations. By actively addressing these biases, we can create more inclusive workplaces where every individual feels valued and has equal opportunities to succeed.
Recap of Key Points
- Unconscious bias refers to automatic associations and attitudes towards certain individuals or groups.
- Confirmation bias, halo effect, stereotyping, and affinity bias are common types of unconscious biases.
- Unconscious bias can lead to unfair judgments and hinder diversity and inclusion efforts.
- Solutions include education, implementing blind processes, and promoting diversity and inclusion.
Importance of Ongoing Efforts to Address Unconscious Bias
Addressing unconscious bias is crucial for fostering an inclusive workplace culture where everyone feels respected and valued. Ongoing efforts are necessary to ensure that biases are continuously identified and challenged, leading to more equitable employee opportunities.
Call to Action for Individuals and Organizations
Individuals must reflect on their biases and actively work towards challenging them. Organizations must prioritize diversity and inclusion initiatives, providing resources, training, and support to address unconscious bias effectively. By working together, we can create workplaces that embrace diversity and provide equal opportunities for all.