Introduction
Effective leadership is crucial in any organization or team. It sets the tone, motivates employees, and drives success. However, leadership is not a one-size-fits-all concept. Different situations require different leadership styles. This is where Fiedler’s Contingency Model of Leadership comes into play. Developed by Fred Fiedler in the 1960s, this model emphasizes the importance of matching leadership style to the situation at hand. By understanding the key components of Fiedler’s model and how they interact, leaders can enhance their effectiveness and adapt to various scenarios.
Understanding the Key Components of Fiedler’s Contingency Model
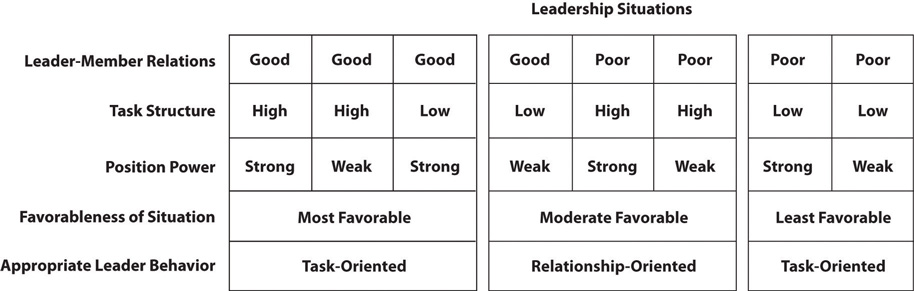
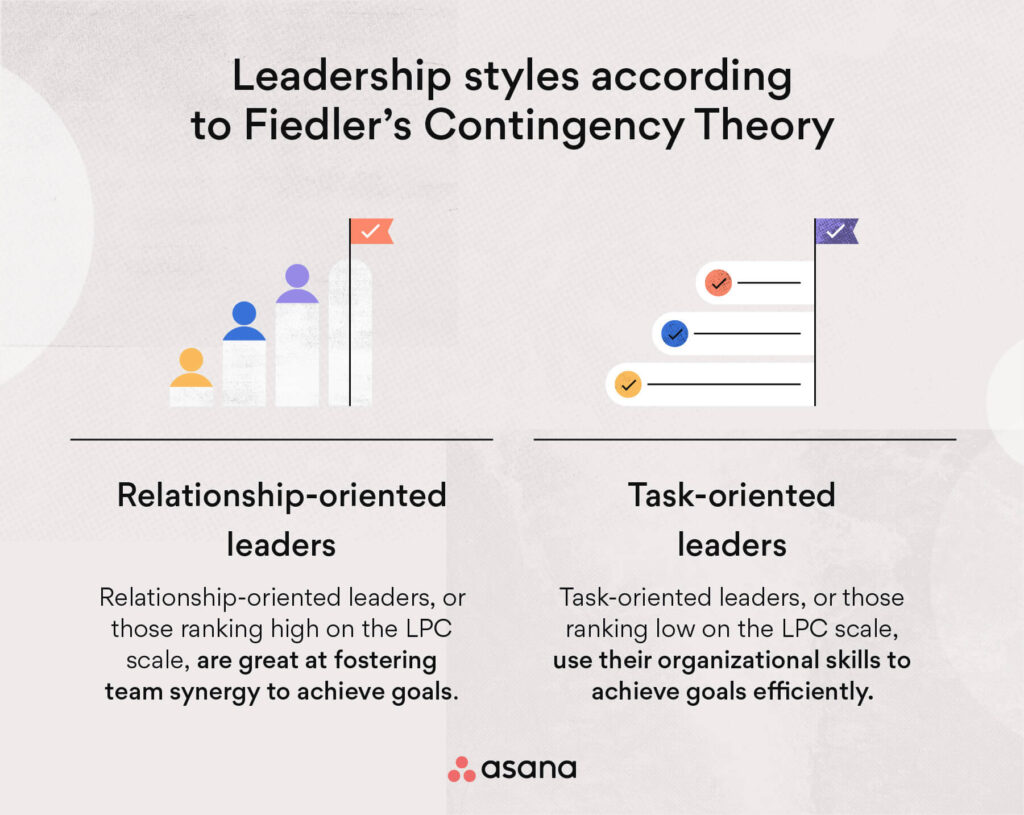
Fiedler’s Contingency Model is based on three key components: leader-member relations, task structure, and position power. Leader-member relations refer to the relationship quality between the leader and group members. Task structure refers to the clarity and structure of the task at hand. Position power refers to the leader’s authority and influence over their subordinates.
The effectiveness of leadership is determined by the interaction of these three components. For example, if leader-member relations are strong, task structure is clear, and position power is high, the leader is more likIf the relationship between the leader and the members is good and the tasks are well-defined, but the leader does not have much power, they might require assistance to be effective.help to be effective.
The Importance of Situational Factors in Fiedler’s Model
Fiedler’s model recognizes that situational factors play a significant role in leadership effectiveness. Situational factors include the task’s nature and the group’s characteristics. For example, a highly structured task with clear goals and guidelines may require a different leadership style than a complex and ambiguous task.
Similarly, the characteristics of the group, such as their level of expertise and motivation, can impact leadership effectiveness. A skilled and motivated group needs less leader’s guidance and supervision, while an inexperienced or less motivated group needs more support.
Fiedler’s model helps leaders adapt to different situations by providing a framework for assessing the situational factors and adjusting their leadership style accordingly. By understanding the specific needs of the task and the group, leaders can tailor their approach to maximize effectiveness.
The Role of Leader-Member Relations in Fiedler’s Model
Leader-member relations are a critical component of Fiedler’s model. The quality of the relationship between the leader and group members can greatly impact leadership effectiveness. When leader-member relations are strong, there is trust, respect, and open communication between the leader and group members. This fosters a positive work environment and enhances collaboration and productivity.
On the other hand, when leader-member relations are poor, there may be a lack of trust, communication barriers, and conflicts. This can hinder teamwork, decrease motivation, and impede progress. In such situations, leaders must improve leader-member relations to enhance effectiveness.
Strategies for improving leader-member relations include building trust through open and honest communication, actively listening to group members’ concerns and ideas, providing support and guidance when needed, and recognizing and rewarding individual and team achievements. Leaders can create a positive work environment that fosters collaboration and productivity by investing time and effort in building strong relationships with group members.
The Significance of Task Structure in Fiedler’s Model
Task structure is another key component of Fiedler’s model. The structure of the task refers to the clarity and guidelines surrounding the task at hand. A highly structured task has clear goals, well-defined roles, and specific guidelines for completion. On the other hand, a task with low structure is ambiguous, lacks clear goals, and has flexible guidelines.
The task structure impacts leadership effectiveness because it determines the level of direction and guidance required from the leader. In a highly structured task, leaders can provide clear instructions and guidelines, allowing group members to work independently and efficiently. In contrast, in a task with low structure, leaders may need to provide more direction, support, and clarification to ensure the task is completed effectively.
Leaders can adapt their leadership style to different task structures by providing clear instructions and guidelines, setting specific goals and expectations, and regularly communicating with group members to ensure understanding and alignment. By understanding the level of structure in the task, leaders can adjust their approach to maximize effectiveness.
The Impact of Position Power on Fiedler’s Model
Position power refers to the authority and influence a leader has over their subordinates. It is another key component of Fiedler’s model. The leader’s position power can greatly impact their effectiveness in leading a group.
When a leader has high position of power, they have the authority and resources to make decisions, allocate tasks, and enforce rules. This gives them the ability to influence and motivate their subordinates effectively. When a leader has low position power, they may struggle to gain the respect and compliance of their subordinates, which can make them less effective.
Leaders can improve their effectiveness and leverage their position power by focusing on three key areas: building credibility and trust with their subordinates, communicating clearly and consistently, and demonstrating fairness and integrity in decision-making.By establishing themselves as competent and trustworthy leaders, they can enhance their position power and influence over their subordinates.
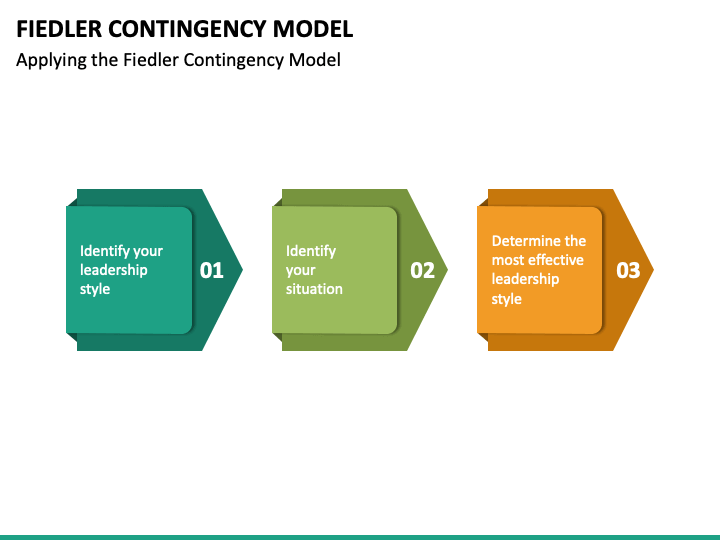
Applying Fiedler’s Model in Real-World Leadership Scenarios
Fiedler’s Contingency Model can be applied in various leadership situations to enhance effectiveness. In a structured task with a strong leader and high position power, the leader can take a more hands-off approach, letting group members work independently and take ownership of their tasks.This promotes autonomy and empowers group members to contribute their expertise and creativity.
In a task with low structure, poor leader-member relations, and low position power, a leader may need to give more direction, support, and guidance.They may need to clarify goals, provide step-by-step instructions, and actively engage with group members to ensure understanding and alignment. This helps overcome the challenges posed by the situation and improves leadership effectiveness.
While Fiedler’s model provides a valuable framework for understanding and adapting leadership style to different situations, it also has its limitations and criticisms.
Criticisms and Limitations of Fiedler’s Contingency Model
One common criticism of Fiedler’s model is that it oversimplifies the complexities of leadership. It assumes that leadership style is fixed and cannot be changed, which may only sometimes be the case. Additionally, the model does not account for the dynamic nature of situations and the potential for situational factors to change over time.
Another limitation of Fiedler’s model is that it relies heavily on self-report measures to assess leader-member relations, task structure, and position power. This can introduce bias and inaccuracies in the assessment process.
Leaders can use Fiedler’s model as a starting point to address these limitations and combine it with other leadership theories and approaches. By taking a holistic view of leadership and considering multiple factors, leaders can develop a more comprehensive understanding of their role and enhance their effectiveness.
Conclusion: The Value of Fiedler’s Model in Developing Effective Leadership Skills
In conclusion, Fiedler’s Contingency Model of Leadership provides a valuable framework for understanding and adapting leadership style to different situations. By considering the key components of leader-member relations, task structure, and position power, leaders can enhance their effectiveness and adapt to various scenarios.
Fiedler’s model emphasizes the importance of situational factors in leadership effectiveness and provides strategies for improving leader-member relations, adapting leadership style to different task structures, and leveraging position power. While the model has its limitations and criticisms, it can be a valuable tool for developing effective leadership skills.
To apply Fiedler’s model, leaders should assess the situational factors, consider their own style and strengths, and adjust their approach accordingly.By continuously learning and adapting, leaders can enhance their effectiveness and drive success in their organizations or teams.